- Title
-
Wnt-PLC-IP3-Connexin-Ca2+ axis maintains ependymal motile cilia in zebrafish spinal cord
- Authors
- Zhang, J., Chandrasekaran, G., Li, W., Kim, D.Y., Jeong, I.Y., Lee, S.H., Liang, T., Bae, J.Y., Choi, I., Kang, H., Maeng, J.S., Kim, M.K., Lee, T., Park, S.W., Kim, M.J., Kim, H.S., Ro, H., Bae, Y.C., Park, H.C., Choi, E.Y., Choi, S.Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
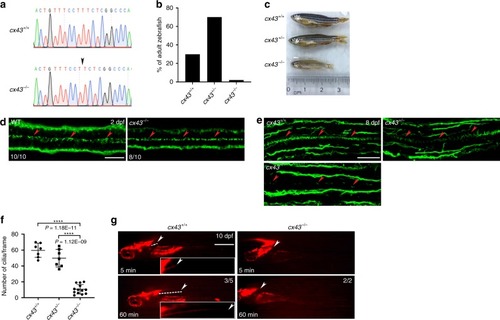
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|