- Title
-
TAF1, associated with intellectual disability in humans, is essential for embryogenesis and regulates neurodevelopmental processes in zebrafish
- Authors
- Gudmundsson, S., Wilbe, M., Filipek-Górniok, B., Molin, A.M., Ekvall, S., Johansson, J., Allalou, A., Gylje, H., Kalscheuer, V.M., Ledin, J., Annerén, G., Bondeson, M.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
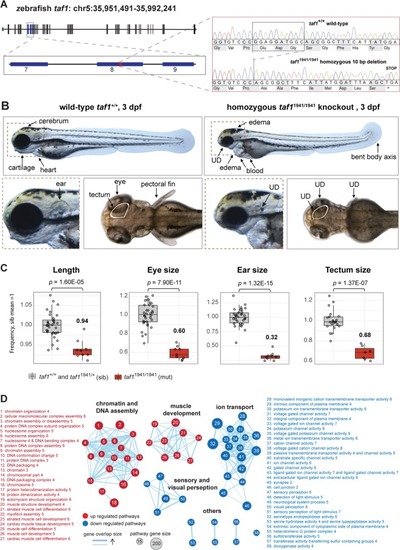
Zebrafish taf1 knockout model revealed an essential function of taf1 during embryogenesis and neurodevelopment. (A) Sequencing results of taf1uu1941/uu1941 F2 zebrafish embryos confirmed a 10 bp deletion in exon 8, which results in a frameshift and a stop codon, p.Glu362Alafs*9. (B) Three days post fertilization (dpf) mutant taf1uu1941/uu1941 (right) zebrafish embryos showed heart and ventricle edema, blood filled cavities, bent body axis, and general underdevelopment (UD) including short pectoral fins, reduced length and underdeveloped cartilage, eyes, and ears. (C) Phenotype quantification demonstrated reduced length, underdevelopment of eyes, ears and tectum when comparing wild-type taf1+/+ and heterozygous taf1uu1941/+ (siblings; sib) with taf1uu1941/uu1941 mutants. Adjusted p-values were generated using Student’s t-test, adjusted with Bonferroni correction. (D) Gene set enrichment analysis of all differentially expressed genes revealed four major themes associated with loss of taf1. Chromatin and DNA assembly as well as muscle development pathways were upregulated (red) and pathways of ion transport as well as sensory and visual perception pathways were downregulated (blue) in taf1uu1941/uu1941 zebrafish embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Comparison of two different taf1 knockout strains. (A) Schematic overview of deletions in two different strains, taf1uu1931/ uu1931 p.(Gly296Leufs*2) and taf1uu1941/ uu1941 p.Glu362Alafs*9. (B) Four zebrafish embryos of both taf1uu1931/ uu1931 and taf1uu1941/ uu1941 at 4 days post-fertilization show a similar abnormal phenotype compared to wild-type taf1 zebrafish (left). The malformations were lethal and included general developmental delay, reduced pigmentation, underdeveloped craniofacial cartilage, cerebral edema, underdeveloped and malformed ears, dorsally bent body axis, heart edema, blood-filled cavities, short pectoral fin, and underdeveloped eyes with coloboma. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|