- Title
-
Microtubules are required for the maintenance of planar cell polarity in monociliated floorplate cells
- Authors
- Mathewson, A.W., Berman, D., Moens, C.B.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
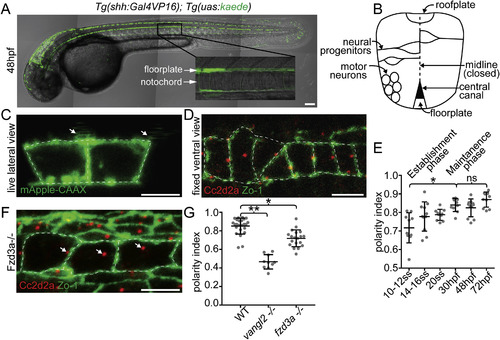
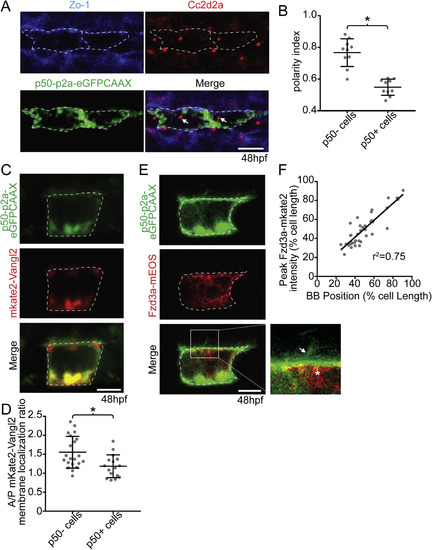
The floorplate is progressively planar polarized in a Vangl2 and Fzd3a-dependent manner. (A) A 48hpf Tg:(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:Kaede)zebrafish embryo expressing Kaede in the floorplate of the neural tube. (B) Schematic of a cross-section of the zebrafish neural tube at 48hpf (not to scale). (C) Single time point from a time lapse of a Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:mApple-CAAX) embryo at 48hpf in which two adjacent floorplate cells are expressing membrane-localized mApple-CAAX (green). Posteriorly localized primary cilia (arrows) appear as squiggles due to their rapid motion. (D) Fixed ventral view of a 48hpf WT floorplate co-immunostained with ZO-1 to mark sub-apical tight junctions (green) and Cc2d2a to mark BBs (red). (E) Quantitation of per embryo polarity index from the 10–12ss through 72hpf. Each dot represents the average polarity index of at least 10 cells within a single embryo. Total N = 62 embryos, 1130 cells. *p < 0.0001; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (F) Fixed ventral view of a 48hpf fzd3a−/− floorplate stained as in D. White dotted line indicates position of cell boundaries, as determined by mApple-CAAX fluorescence (C) or ZO-1 staining (D,F), arrows indicate BB positions. (G) BB polarity indices of WT, vangl2−/− and fzd3a−/− embryos at 48hpf. Each dot represents the average polarity index of at least 10 cells within a single embryo. Total N = 54 embryos, 448 cells; **p < 0.0001; *p = 0.0018; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. Anterior is to left in all images. Scale bars: 100 μm (A) or 5 μm (C,D,F). |
|
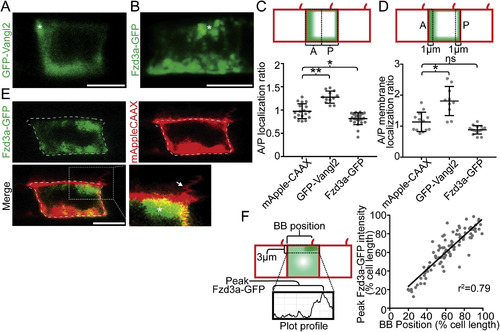
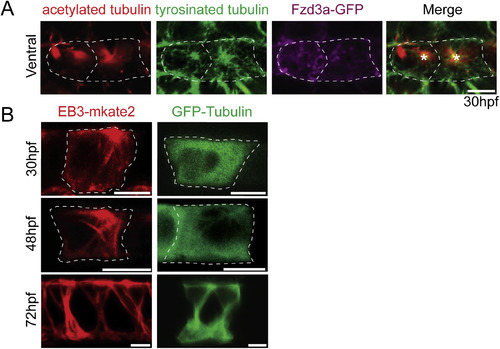
Vangl2 and Fzd3a localization in the floorplate. (A–B) Live lateral views of 48hpf (A) Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:GFP-Vangl2) and (B) Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:Fzd3a-GFP) single expressing floorplate cells. Asterisks indicate positions of fusion protein (green) concentration along the apical membrane. (C) Schematic: diagram indicating how total fusion protein localization was measured on anterior vs. posterior cell halves. Graph: quantitation of anterior vs. posterior fusion protein localization in isolated expressing cells. Each dot represents the ratio of the mean fluorescence level within a single cell anterior half divided by the mean fluorescence level of its posterior half. N = 57 embryos, 152 cells; **p = 0.0035; *p = 0.0266; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (D) Schematic: diagram indicating how fusion protein localization was measured on anterior vs. posterior membranes. Graph: quantitation of anterior vs. posterior fusion protein membrane localization in isolated expressing cells. Each dot represents the ratio of the mean fluorescence level along the anterior membrane a single cell divided by the mean fluorescence level along its posterior membrane. N = 39 embryos, 106 cells; *p = 0.0154; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (E) Live lateral views of a 48hpf Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:Fzd3a-GFP); Tg(uas:mAppleCAAX) dual transgene expressing floorplate cell. Inset: magnified view of the posterior apical cellular membrane where Fzd3a-GFP (green, asterisk) is concentrated near the base of the primary cilia (red apical extension, arrow). Approximate cell boundaries, as determined by mAppleCAAX expression, indicated by white dotted lines. (F) Schematic: diagram indicating how apically localized cytosolic Fzd3a-GFP levels were quantified (see methods) Graph: correspondence of Fzd3a-GFP peak localization with primary cilium position. Each point corresponds to measurements from a single cell. r2 = 0.79. Anterior to left in all images. Scale bars: 5 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
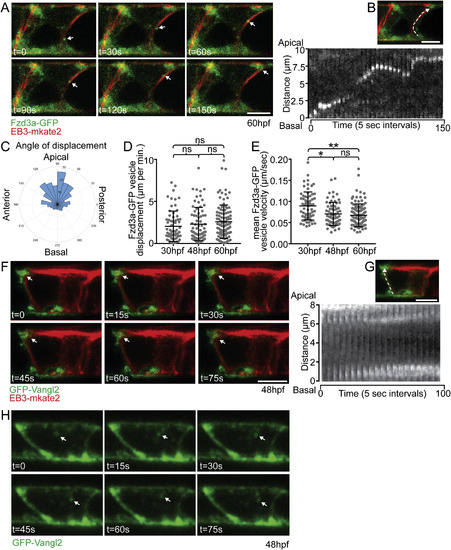
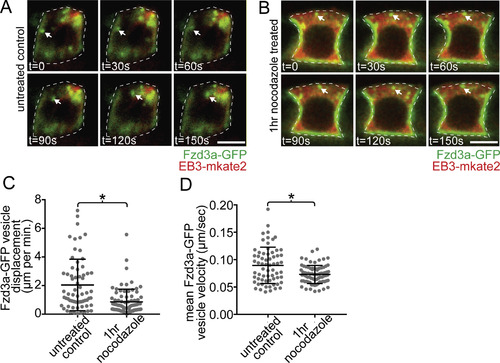
Fzd3a and Vangl2 trafficking in the floorplate. (A) Single timepoints from a time lapse movie of a 60hpf Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:Fzd3a-GFP); Tg(uas:EB3-mkate2) dual transgene expressing floorplate cell in lateral view showing EB3-mKate2-labeled MTs (red) and Fzd3a-GFP vesicles (green). Arrows track an individual Fzd3a-GFP vesicle as it moves in the apical and posterior direction along a MT. (B) inset image: overlay shows measurement path used to generate kymograph. Kymograph: plot showing the apically directed movement of a single Fzd3a-GFP vesicle along a MT polymer. (C–E) Fzd3a-GFP vesicular movements were tracked during 5-s interval time lapse movies of laterally-viewed floorplate cells in Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:Fzd3a-GFP); Tg(uas:EB3-mkate2) embryos at 30, 48, and 60hpf. N = 240 vesicles, 89 cells, 9 embryos. (C) Rose plot of final relative displacement angles of individual Fzd3a-GFP containing vesicles between first and last measured positions. (D) Quantitation of individual Fzd3a-GFP vesicle displacement distances between first and last timepoint measured, divided by total tracking time. Significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (E) Quantitation of average velocities of individual Fzd3a-GFP vesicles. **p < 0.0001; *p = 0.0023; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (F) Single timepoints from a time lapse movie of a 48hpf Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:GFP-Vangl2); Tg(uas:EB3-mkate2)dual transgene expressing floorplate cell in lateral view. MTs are labeled by EB3-mkate2 (red) and GFP-Vangl2 is shown in green. Arrows indicate GFP-Vangl2 anterior apical localization, which does not change over time. (G) inset image: overlay showing measurement path used to generate kymograph. Kymograph showing the absence of GFP-Vangl2 trafficking along the MT polymer. (H) Single timepoints of a Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:GFP-Vangl2) floorplate cell demonstrating a rare example of detectable GFP-Vangl2 cytosolic puncta. Anterior to left in all images. Approximate cell boundaries indicated by white dotted lines. Scale bars: 5 μm. |
|
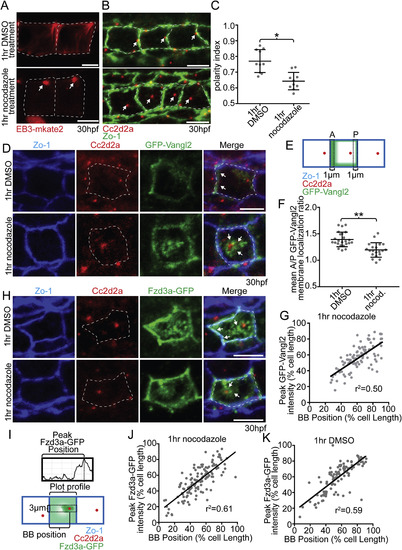
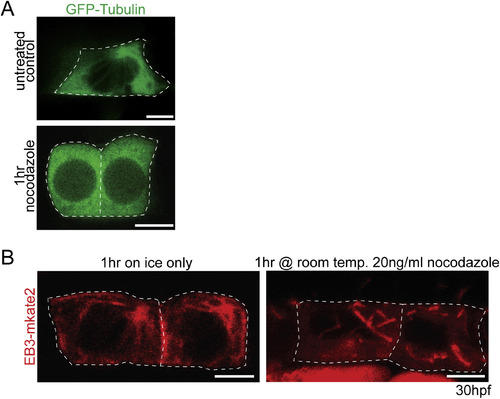
Microtubules are required to maintain floorplate PCP. (A) Live lateral views of floorplate cells expressing Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:EB3-mkate2) at 30 hpf. Upon nocodazole treatment EB3-mkate2 labeled MTs collapse to subapical foci near the BB (arrows). (B) Ventral views of Cc2d2a (red) and Zo-1 (green) immunostaining Arrows indicate position of BBs. Nocodazole treatment disrupts the posterior localization of BBs. (C) Quantitation of per embryo average BB polarity index after 1hr DMSO treatment (control) or 1hr nocodazole treatment. N = 200 cells, 20 embryos; *p = 0.0003; significance was determined with Mann-Whitney test. (D) Ventral views of 30hpf Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:GFP-Vangl2) embryos. White dotted lines indicate cell boundaries based on ZO-1 staining. Arrows indicate GFP-Vangl2 localization at the anterior membrane in controls and around the BB in nocodazole-treated embryos. (E) Diagram illustrating how anterior and posterior membrane levels of GFP-Vangl2 were measured in fixed ventral floorplate images. (F) Quantitation of per embryo average GFP-Vangl2 anterior vs. posterior membrane localization ratios in isolated floorplate cells expressing Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:GFP-Vangl2). N = 416 cells, 66 embryos; **p < 0.0001, *p = 0.0013; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (G) Graph of the correlation between GFP-Vangl2 and BB localization. After 1hr nocodazole treatment peak GFP-Vangl2 intensity correlates with the position of the BB N = 10 embryos, 100 cells, r2 = 0.50. (H) Ventral views of floorplate cells at 30 hpf immunostained for Fzd3a-GFP (green), Zo-1 (blue) and Cc2d2a (red) after 1hr DMSO treatment (control) or 1hr nocodazole treatment. (I) Diagram illustrating how peak Fzd3a-GFP localization and BB positions were measured. BB distance from anterior membrane was measured compared to overall anterior-posterior cell length. A 3 μm wide ROI centered on the position of the BB was drawn from anterior to posterior membranes. The “plot profile” tool in ImageJ was used to measure average GFP levels across the anterior to posterior cell axis. (J,K) Correlation between Fzd3a-GFP localization and BB position in nocodazole-treated and control floorplate cells. Each data point represents the measurements from a single cell. J: N = 100 cells, 10 embryos; r2 = 0.61; K: N = 100 cells, 10 embryos; r2 = 0.59. Scale bars: 5 μm. |
|
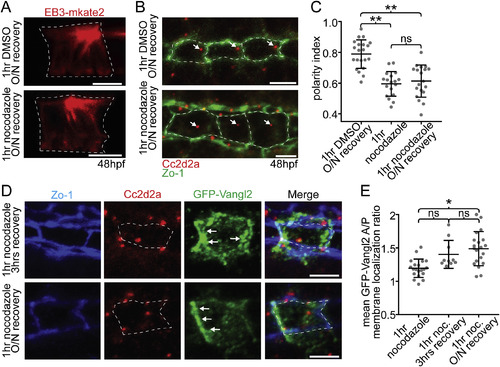
Maintenance of PCP protein polarity does not depend on a polarized BB. (A) EB3-mkate localization to centrosomal MTs recovers after recovery from nocodazole treatment (compare to Fig. 4A). (B) Ventral images of fixed 48hpf WT floorplates coimmunostained for Cc2d2a (red) and ZO-1 (green). BBs (arrows) remain delocalized after recovery from nocodazole treatment. (C) Quantitation of per embryo average BB polarity index in WT embryos that were treated with either DMSO (control) or cold 5 ng/μl nocodazole for 1hr and then either fixed immediately or allowed to recover overnight. N = 615 cells, 58 embryos; **p < 0.0001; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. (D) Ventral images of fixed GFP-Vangl2 expressing floorplate cells in Tg(shh:gal4); Tg(uas:GFP-Vangl2) embryos that were treated with nocodazole for 1hr and then recovered for either 3 hrs or overnight. Arrows indicate recovery of asymmetric GFP-Vangl2 localization. Compare to Fig. 4D. (E) Quantitation of GFP-Vangl2 anterior vs. posterior membrane localization ratios after 1hr nocodazole treatment followed by different recovery periods. N = 236 cells, 29 embryos; *p = 0.0004; significance was determined with a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison. White dotted lines mark approximate cell boundaries, based on ZO-1 staining of tight junctions. Scale bars: 5 μm. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 452(1), Mathewson, A.W., Berman, D., Moens, C.B., Microtubules are required for the maintenance of planar cell polarity in monociliated floorplate cells, 21-33, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.