- Title
-
Targeted disruption of the endogenous zebrafish rhodopsin locus as models of rapid rod photoreceptor degeneration.
- Authors
- Zelinka, C.P., Sotolongo-Lopez, M., Fadool, J.M.
- Source
|
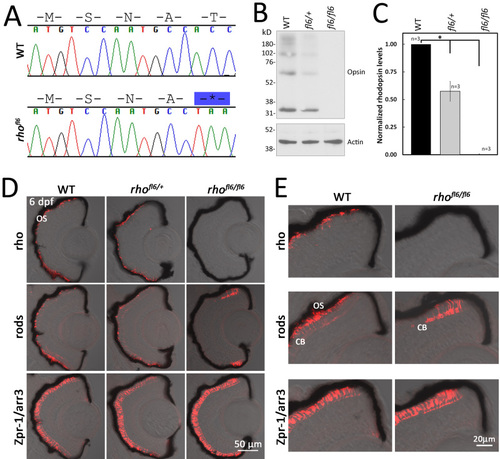
DNA sequence and histology of rhofl6 encoding a premature stop codon p.17T*. A: Chromatograms overlaid with amino acid sequences comparing WT and rhofl6 allele encoding p.17T*. B: Representative immunoblot analysis of detergent-soluble extracts of retinas from WT, heterozygous rhofl6/+, or homozygous rhofl6/fl6 adults separated by SDS–PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with the 1D1 mab against Rho or mab AC-74 against B-Actin. Immunolabeling of opsin observed as the monomer at 32 kDa and multimers at 64, and 98 kDa were reduced in the heterozygous rhofl6/+ sample and not detected in the homozygous rhofl6/fl6 retina. C: Bar graph of normalized densitometry of immunoblot labeling for Rho (n = 3 animals per genotype), * p<0.025, Kruskal-Wallis test. D: Confocal images of cryosections of retinas from 6 dpf WT, heterozygous rhofl6/+, or homozygous rhofl6/fl6 mutants labeled with antibodies to Rho (1D1, red), rods (4C12, red), or Zpr-1/Arr3a, a selective marker expressed by red/green cones (Zpr-1, red) overlaid with bright-field microscopy. Note the lack of labeling for rods in the central retina and differential labeling for Rho/1D1 and rods/4C12 near the retinal margin of rhofl6/fl6 homozygous larvae, suggesting that rhofl6 is a null allele. E: Higher magnification images of immunolabeling of the dorsal retinal margin WT and homozygous rhofl6/fl6 mutants showing the lack of immunolabeling for Rho, an absence of outer segments (OS), but labeling of the cell bodies (CB) by 4C12 in the homozygous mutant larvae. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
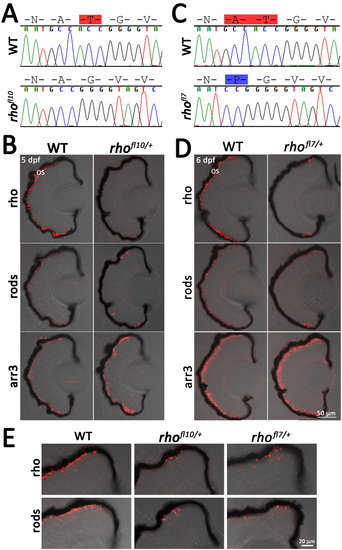
Disruption of the N-linked glycosylation sequence in rhofl10 and rhofl7 leads to rod degeneration. A, C: Chromatograms overlaid with amino acid sequences comparing WT, rhofl10, and rhofl7 alleles, disrupting the conserved NXT consensus glycosylation sequence at N15. Red highlights deleted amino acids, while blue highlights insertions. B, D: Confocal images of serial retinal cryosections of 5 or 6 dpf WT or heterozygous rhofl10/+ and rhofl7/+ mutants labeled with antibodies to Rho (1D1, red), rods (4C12, red), and Arr3a (Zpr-1, red) overlaid with bright-field microscopy reveal loss of rod-specific labeling in the central retina. E: Higher magnification images of the dorsal retinal margin from WT, heterozygous rhofl10/+, or rhofl7/+ mutants showing sparse immunolabeling for Rho and rods. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
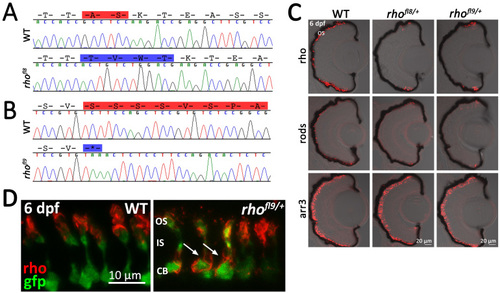
Alteration of conserved C-terminal domains in rhofl8 and rhofl9. A, B: Chromatograms overlaid with amino acid sequences of 3′ rh1-1 in WT, the rhofl8 allele, and the rhofl9 allele. Predicted amino acid deletions are highlighted in red on the WT sequences; insertions are highlighted in blue on the mutant sequence. C: Confocal images of retinal sections of 6 dpf WT or heterozygous rhofl8/+ or rhofl9/+ larvae labeled with antibodies to Rho (1D1, red), rods (4C12, red), or Arr3a (Zpr-1, red) overlaid with bright-field microscopy. D: High magnification confocal images of 6 dpf WT or heterozygous rhofl9/+ larvae showing the rod-specific expression of EGFP (gfp, green) and immunolabeling for Rho (1D1, red). In WT retinas, the Rho immunolabeling is localized to the outer segment (OS), while in the mutant, Rho immunolabeling is localized to the inner segment (IS) and the cell body (CB; arrows). |
|
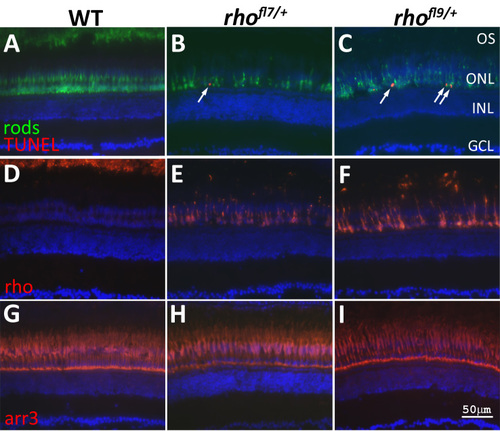
rhofl7 and rhofl9 lead to increased TUNEL in adults. Retinal sections of WT (A,D,G) or heterozygous rhofl7/+ (B,E,H) and rhofl9/+ (C,F,I) adult zebrafish immunolabeled with antibodies to rods (4C12, green, A-C), Rho (1D1, red, D-F), or red/green cones (Arr3a/Zpr-1, red, G-I) and stained with TUNEL (red, A-C). All sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Immunolabeling for rods reveals fewer, less regularly arranged cells in the mutants compared to the WT. TUNEL-positive nuclei (arrows), positioned along the proximal region of the ONL, are only observed in the mutant retinas (A-C). In WT retinas, Rho immunolabeling is restricted to the ROS at the top of the panel D. Immunolabeling in rhofl7/+ and rhofl9/+ adults is localized to the cell bodies, and no outer segments are evident (E-F). Immunolabeling for red and green cones was indistinguishable across the samples (G-H). Abbreviations: ganglion cell layer, GCL; inner nuclear layer, INL; outer nuclear layer, ONL. |