- Title
-
Developmental expression of the slurp-like1/ly2.3/ly97.3 and slurp-like2/ly2.2/ly97.2 genes during zebrafish early embryogenesis
- Authors
- Kawahara, A., Morita, H., Yanagi, K., Ishizaka, T., Taimatsu, K., Ohga, R.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
The spatial expression pattern of slurp-like1 during early development. (A) 1-cell stage. (B) Dome stage. (C) Shield stage. (D) Bud stage. (E) 5-somite stage. (F) 10-somite stage. (G) 15-somite stage. (H) 20-somite stage. (I, J) 24 hpf stage. (K) 48 hpf stage. (L, M) 72 hpf stage. All pictures except for (J: transverse section) and (M: dorsal view) show the lateral view. (D–K) Anterior to the left, dorsal up. slurp-like1 expression was broadly expressed at the 1-cell, dome, shield and bud stages, while the slurp-like1 gene was detected in the yolk at the 5-somite, 10-somite, 15-somite and 20-somite stages. At 24 hpf (I, J), slurp-like1 is expressed in the floor plate (arrow) of the neural tube (dotted line) and in the hypochord (arrowhead) of the notochord (asterisk). At 48 hpf (K) and 72 hpf (L, M), slurp-like1 is expressed in the liver (red arrowhead) and intestinal bulb (blue arrowhead). Scale bars, 100 μm for A-K, L and M and 50 μm for J. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The spatial expression pattern of slurp-like2 during early development. (A) 1-cell stage. (B) Dome stage. (C) Shield stage. (D) Bud stage. (E) 5-somite stage. (F) 10-somite stage. (G) 15-somite stage. (H) 20-somite stage. (I) 24 hpf stage. (J) 48 hpf stage. (K, M) 72 hpf stage. All pictures except for L and M (dorsal view) show the lateral view. (D–K) Anterior to the left, dorsal up. slurp-like2 expression was marginal at the 1-cell, dome, shield and bud stages, while the slurp-like2 gene was weakly detected in the yolk at the 5-somite, 10-somite, 15-somite and 20-somite stages. At the 24 hpf (I, L) and 48 hpf (J) stages, the slurp-like2 gene was expressed in the midbrain (cross) and hindbrain (asterisk). At the 72 hpf stage (K, M), the slurp-like2 gene was expressed in the liver (red arrowhead) and pancreas (green arrowhead). Scale bars, 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Effect of a Notch signaling inhibitor, DAPT, on slurp-like1 expression. (A–D) Wild-type embryos at 6 hpf (A, B) were exposed to 100 μM DAPT (Notch signal inhibitor: B) or the same volume of DMSO (control: A) and incubated at 28.5 °C until 24 hpf, while wild-type embryos at 16 hpf (C, D) were incubated with 100 μM DAPT (D) or DMSO (C) and incubated until 24 hpf. The expression of slurp-like1 was examined by WISH using the antisense slurp-like1 RNA probe. The slurp-like1 expression in the hypochord (arrowhead) was strongly inhibited in the embryos treated with early DAPT treatment (B; 6 hpf), while its expression was partly inhibited in the embryos with late DAPT treatment (D; 16 hpf). The slurp-like1 expression in the floor plate (arrow) was not affected. Scale bars, 100 μm. |
|
Transverse sections of slurp-like1- and slurp-like2-stained embryos at the 5-somite stage. Both genes were weakly expressed in the yolk syncytial layer (arrows) and endoderm (arrowheads). Scale bars, 100 mm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
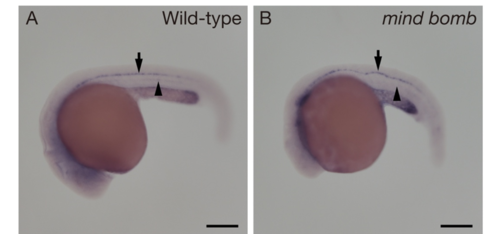
The expression of slurp-like1 in mind bomb (mib) mutant. The slurp-like1 expression in the hypochord (arrowheads) was inhibited in the Notch signal-defective mib mutant, while the slurp-like1 expression was detected in the floor plate (arrows). Scale bars, 200 mm. |
|
Effect of a Shh signaling inhibitor, cyclopamine, on slurp-like1 expression. (A, B) Wild-type embryos at 3 hpf were exposed to 100 mM cyclopmaine (Shh signal inhibitor: B) or the same volume of ethanol (control: A) and incubated at 28.5 °C until 24 hpf. Treatment with cyclopamine caused embryo malformations and a reduction of slurp-like1 expression in the floor plate and hypochord. Scale bars, 200 mm. |
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 30, Kawahara, A., Morita, H., Yanagi, K., Ishizaka, T., Taimatsu, K., Ohga, R., Developmental expression of the slurp-like1/ly2.3/ly97.3 and slurp-like2/ly2.2/ly97.2 genes during zebrafish early embryogenesis, 32-36, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns