- Title
-
Neuregulin-1 is essential for nerve plexus formation during cardiac maturation
- Authors
- Brown, D., Samsa, L.A., Ito, C., Ma, H., Batres, K., Arnaout, R., Qian, L., Liu, J.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Cell. Mol. Med.
|
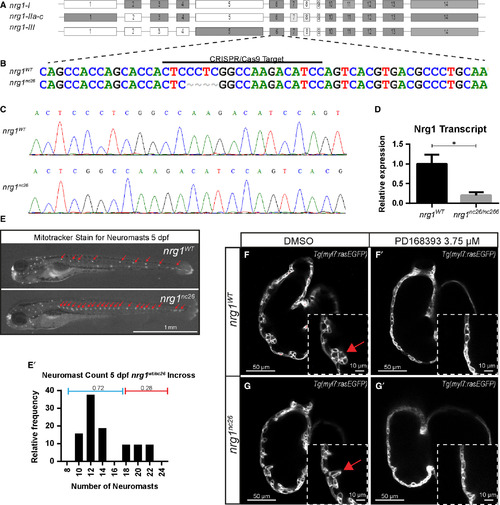
Generation and validation of nrg1nc26 allele. (A) Gene structure of zebrafish nrg1 (exons drawn to scale). Alternative splicing produces three primary isoforms, nrg1‐I, nrg1‐IIa‐c and nrg1‐III. (B, C) CRISPR/Cas9 targeting at Exon 6 produced the nrg1nc26 allele with a four amino acid deletion. (D) Detection of nrg1 mRNA transcripts spanning Exons 6–10 by qPCR; statistical significance determined by t‐test, *P < 0.05. (E) Representative nrg1wt and nrg1nc26/nc26 clutchmates stained with Mitotracker Red to detect neuromasts in the developing lateral line at 4–5 dpf. Red arrows designate neuromasts. (E’) Relative frequency of the number of neuromasts counted in embryos from heterozygous incrosses of nrg1wt/nc26 fish, N > 24 larvae. (F‐G’) Representative confocal optical mid‐chamber slice of the ventricle at 3–4 dpf in larvae carrying Tg(myl7:rasGFP) cardiomyocyte reporters and treated with DMSO or 3.75 μM ErbB2 inhibitor PD168393. Boxes include high‐resolution image of the outer curvature. Red arrows point to developing trabeculae.
|
|
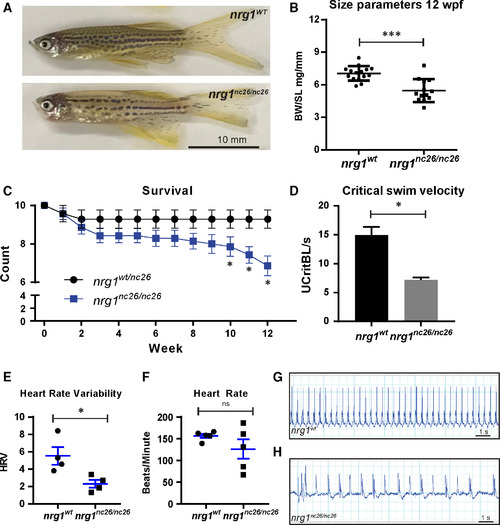
Adult cardiovascular consequences in nrg1nc26 mutants. (A) Gross appearance of adult nrg1WT and nrg1nc26/nc26 fish. (B) Body mass normalized to standard length in adult fish SL 20 ± 2, N = 12. (C) Critical swimming velocity of adult fish SL = 15 ± 1 N = 8. (D) Weekly survival of nrg1WT and nrg1nc26/nc26 clutchmates reared separately in N = 7 tanks of 10 fish each. (E, F) Heart rate variance (HRV) and heart rate in beats per minute measured via electrocardiogram, SL = 15 ± 1, N = 3–5. (G, H) Representative electrocardiographs from nrg1WT and nrg1nc26/nc26 fish. Statistical significance determined by t‐test, ns = not significant, P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
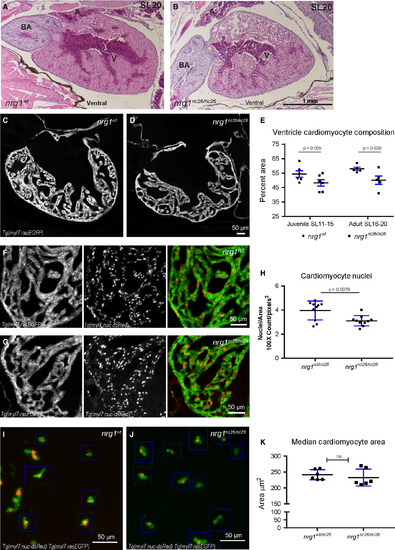
Reduced trabecular myocardium in nrg1nc26 mutants due to lower cellularity. (A) Representative cross section of the heart in H&E‐stained section of formaldehyde‐fixed, paraffin‐embedded nrg1WT and nrg1nc26/nc26 adult fish at SL = 20, N = 3. BA = Bulbous Arteriosus, V = Ventricle, A = Atrium. Scale bar 100 μm. (C–E) Intracardiac density measured from confocal 9.6 μm cross section of hearts from Tg(myl7:rasGFP) fish. (C, D) Representative images, SL = 13. (E) Intracardiac myocardial density quantified as the per cent area occupied by rasGFP+ cells in the outer curvature relative. (F–H) Cardiomyocyte numbers measured from confocal 9.6 μm cross section of hearts from double transgenic Tg(myl7:rasGFP);Tg(myl7:nuc‐dsRED) fish (F, G) Representative images, SL = 13. (H) Relative number of cardiomyocytes measured as from cross sections as the ratio of dsRED‐positive nuclei to rasGFP‐positive pixels in fish SL11‐SL20. (I–K) Cardiomyocyte size measured in mononuclear cells dissociated from Tg(myl7:rasGFP);Tg(myl7:nuc‐dsRED) hearts. (I, J) Representative dissociated cell preparations. (K) Median area of N > 200 cells per sample with 1–2 hearts per sample, N = 6 biological replicates.
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
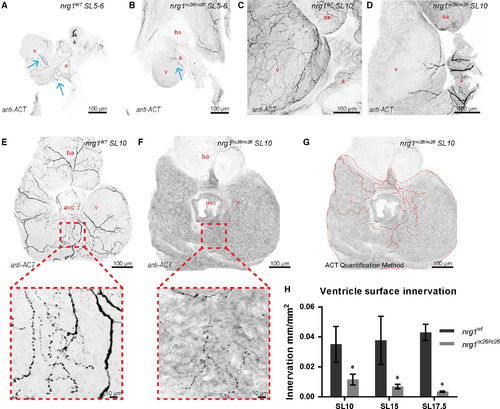
Reduced ventricle surface innervation from juvenile to adult stages. (A–F) Representative z‐projections of confocal images of axons stained with anti‐acetylated α‐tubulin. (A, B) Larvae at SL 5–6 were fixed and stained in situ with the heart partially dissected. (C, D) Juvenile hearts at SL 10 demonstrated partial atrial and limited ventricular innervation in nrg1nc26/nc26 hearts. (E, F) Maximum intensity, z‐project of confocal images of dorsal surface of ventricle with atrium removed at SL10 with magnified view of representative innervated regions. (G, H) Quantification of ventricle surface innervation using methodology illustrated in (G) as the quotient of the total length of axons and ventricle surface. (H) Innervation quantified in N > 3 hearts at SL 10 ± 1, SL 15 ± 1 and SL 17.5 ± 1. Abbreviations a = atrium, v = ventricle, ba = bulbous arteriosus. Scale bars are 100 μm. Student's t‐test mutant compared to wild‐type. Error bars are S.E.M. *P = 0.01–0.05. Blue arrows point to axons.
PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
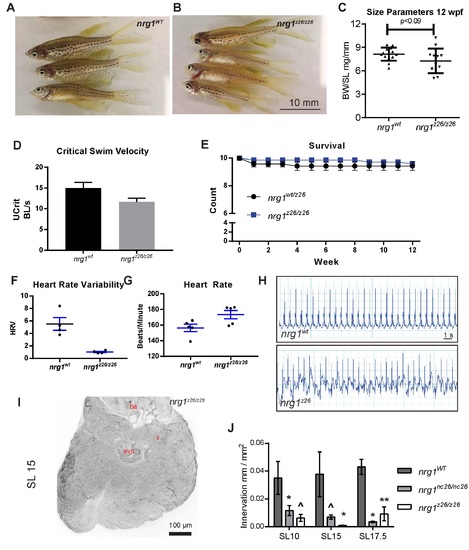
Adult cardiovascular consequences in nrg1z26, nrg1‐III specific allele. (A) Gross appearance of adult nrg1WT and nrg1z26/z26 fish. (B) Body mass normalized to standard length in adult fish SL 20±2, N=12. (C) Critical swimming speed of adult fish SL=15±1 N=8. (D) Weekly survival of nrg1WT and nrg1z26/z26 clutchmates reared separately in N=7 tanks of 10 fish each. (E‐F) Heart rate variance (HRV) and heart rate in beats per minute measured via electrocardiogram, SL=15±1, N=3–5. (G‐H) Representative electrocardiographs from nrg1WT and nrg1z26/z26 fish. (I) Representative z‐projections of confocal images anti‐acetylated α‐tubulin axon staining on the dorsal surface of SL 15 fish with the atrium removed. (J) Quantification of ventricle surface innervation as the quotient of the total length of axons and ventricle surface in N>3 hearts at SL 10±1, SL 15±1, and SL 17.5±1. Abbreviations a=atrium, v=ventricle, ba= bulbous arteriosus. Student's T‐test mutant compared to wild type. Error bars are S.E.M. ^P=0.05‐0.10, *P=0.01‐0.05, **P=0.001–0.01. |