- Title
-
Dopaminergic neuronal loss and dopamine-dependent locomotor defects in fbxo7-deficient zebrafish
- Authors
- Zhao, T., Zondervan-van der Linde, H., Severijnen, L.A., Oostra, B.A., Willemsen, R., and Bonifati, V.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
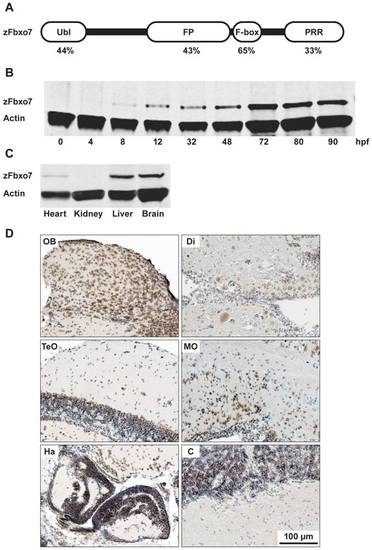
Characterization of the zFbxo7 protein in zebrafish. (A) Schematic representation of the zFbxo7 functional domains. The values underneath each domain indicate the amino acids identity between zFbxo7 and hFBXO7 (isoform1). Ubl: ubiquitin-like domain; FP: FBXO7/ PI31 domain; F-box: F-box motif; PRR: proline rich domain. (B) Western blot analysis of the zFbxo7 protein expression at different developmental stages. (C) Western blot analysis of zFbxo7 protein expression in different tissues of eight-month-old adult zebrafish. Actin was used as reference protein.(D) Immunostaining of the zFbxo7 protein in eight-month-old zebrafish brain areas. The zFbxo7 immunoreactivity is shown in brown, while the cell nuclei are counterstained in blue using hematoxylin. The following areas are shown: olfactory bulb (OB), diencephalon (Di), optic tectum (TeO), medulla oblongata (MO), habenula (Ha), and cerebellum (C). Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
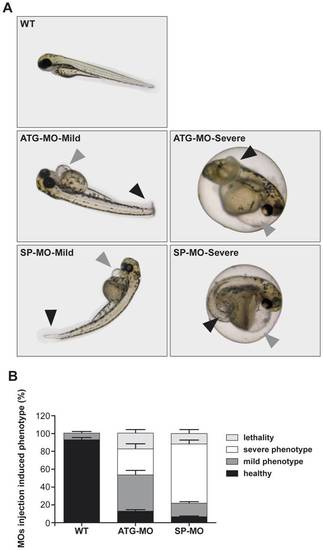
zFbxo7 knock down results in developmental defects. (A) Representative images of zebrafish wild type and morphants. Injection of ATG-MO or SP-MO induced a range of phenotypes, which were grouped in mild and severe, including curly tails (black arrowheads), heart edema and heart malformations (grey arrowheads). (B) Percentages of healthy phenotype, mild phenotype abnormalities, severe phenotype abnormalities and lethality among uninjected control (WT) and MOs-injected morphants. zFbxo7 knock down results in decreased zFbxo7 protein expression PHENOTYPE:
|
|
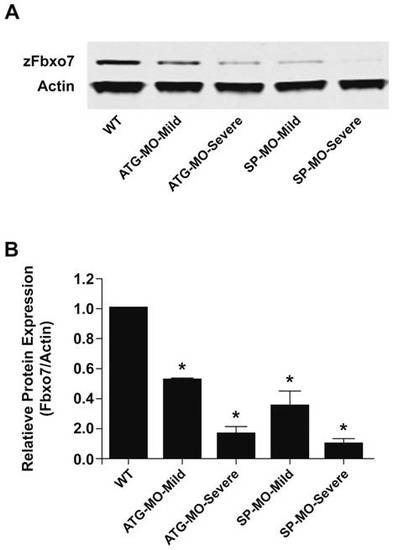
zFbxo7 knock down results in decreased zFbxo7 protein expression. (A) Western blot of the zFbxo7 protein at 72 hpf in uninjected control (WT) and MOs-injected morphants which showed mild or severe phenotype abnormalities. (B) Quantification of the zFbxo7 protein levels is shown in panel A (Odyssey software). Data were collected from three independent experiments, P<0.01. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
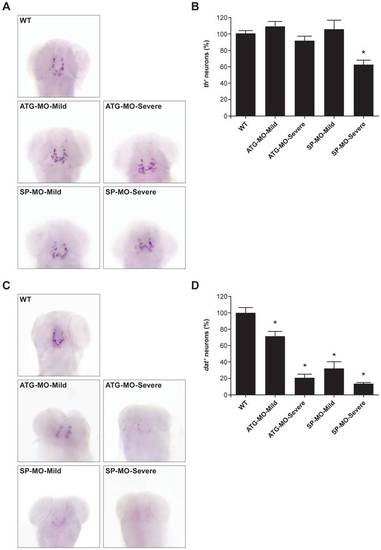
zFbxo7 knock down results in dopaminergic neuronal cell loss. The brain catecholaminergic neurons were visualized by whole-mount in situ hybridization using antisense RNA probes specific for tyrosine hydroxylase (th, panel A) or dopamine transporter (dat, panel C). Number of neurons were counted manually and normalized to the counts in wild type zebrafish (panels B and D). * P<0.01 EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
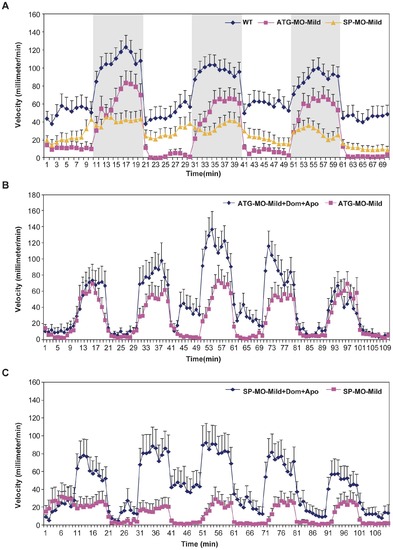
zFbxo7 knock down results in locomotor defects, which are improved by apomorphine. The movements of WT zebrafish, ATG-MO-Mild and SP-MO-Mild morphants were recorded during three cycles of 10-minutes light/10-minutes darkness (periods of darkness are shown in grey). Compared with WT, morphants showed significantly decreased velocity in both light and dark phases (P<0.01, panel A), which were significantly improved by treatment with apomorphine (P<0.01 in the dark phase, panels B and C). Dom: domperidone. Apo: apomorphine. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
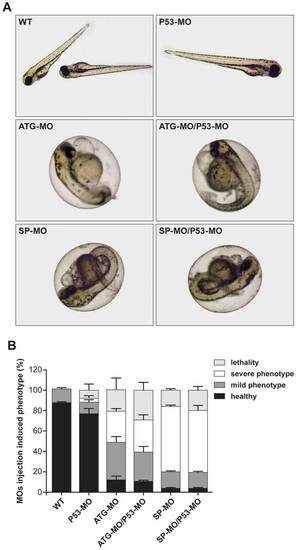
Off-target effects due to MO-induced p53 activation are not detected. (A) Representative images of zebrafish embryos treated with single MO injection (ATG-MO, SP-MO or P53-MO) or co-injection (ATG-MO/P53-MO or SP-MO/P53-MO). (B) Percentage of healthy phenotype, mild phenotype abnormalities, severe phenotype abnormalities and lethality among uninjected control (WT), single injected morphants and co-injected morphants. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
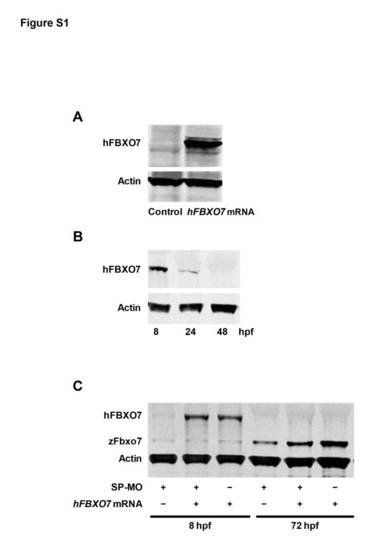
Expression of endogenous zFbxo7 and exogenous hFBXO7 occurs in different time points during the zebrafish development.(A) Western blot analysis after in vitro protein translation of the hFBXO7 mRNA. A band of the expected size of the hFbxo7 protein was detected, validating the hFBXO7 mRNA as a rescuing template mRNA. An empty lane (Control) shows the reaction product after omitting the hFBXO7 mRNA template. (B) Time course of the expression of exogenous hFBXO7 in vivo in wild type embryos.The hFBXO7 mRNA was injected into one-cell stage embryos, and the expression of hFBXO7 was probed at 8, 24 and 48 hpf by Western blot. The expression of hFBXO7 was already markedly lower at 24 hpf, and was undetectable at 48 hpf.(C) The expression of exogenous hFBXO7 and endogenous zFbxo7 in vivo in zebrafish embryos with or without co-injection of SP-MO. The hFBXO7 mRNA and/or SP-MO were injected into one-cell stage embryos, and the expression of proteins was probed at 8 and 72 hpf by Western blot. The expression of the endogenous zFbxo7 was maximal at 72 hpf, when the exogenous hFBXO7 was undetectable. |