- Title
-
Localized Products of futile cycle/ lrmp Promote Centrosome-Nucleus Attachment in the Zebrafish Zygote
- Authors
- Lindeman, R.E., and Pelegri, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Curr. Biol.
|
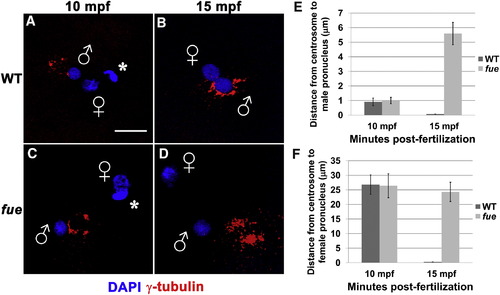
Centrosomes Fail to Attach to Pronuclear Envelopes in fue Embryos (A–D) In vitro fertilized embryos from WT and fue females fixed and labeled for centrosomes (γ-tubulin antibody, red) and DNA (DAPI, blue) at 10 (A and C) and 15 mpf (B and D). Asterisks indicate polar bodies, and male and female pronuclei are indicated with symbols. Scale bar represents 20 μm and applies to all panels. Images are projections from confocal z stacks. (E and F) Distance between centrosomal γ-tubulin labeling and male or female pronuclear envelopes quantified at 10 and 15 mpf. Error bars indicate ±1 SE. See also Figure S1 and Movies S1 and S2. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
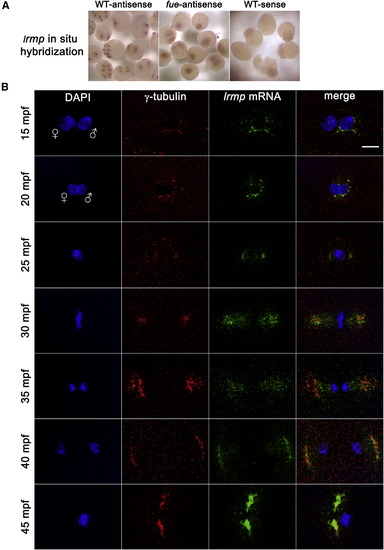
lrmp Transcripts Show Dynamic Localization Patterns Lost in fue Mutants (A) Chromogenic in situ hybridization with lrmp antisense probes in WT (left) and fue mutants (center) and negative control sense probes (right). (B) WT embryos fixed at 5 min intervals and labeled with γ-tubulin antibody (red) and DAPI (blue), in combination with fluorescent in situ detection of lrmp mRNA (green). Scale bar represents 20 μm and applies to all panels in (B). See also Figure S3. |
|
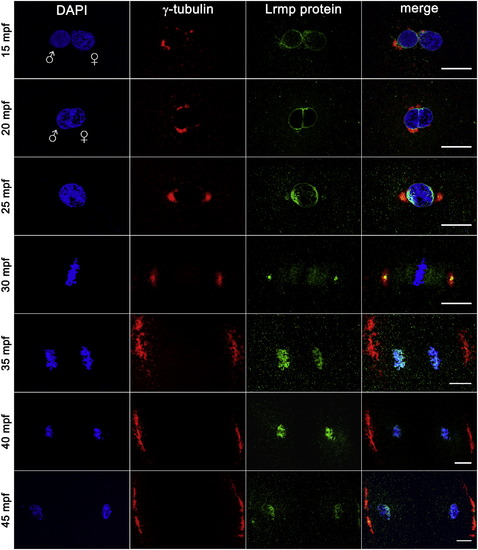
Lrmp Protein Localizes to Nuclear Membranes and Subregions of the Mitotic Apparatus WT embryos fixed at 5 min intervals and labeled with γ-tubulin antibody (red), anti-LrmpMD antiserum (green), and DAPI (blue). Scale bars represent 20 μm. See also Figure S4. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
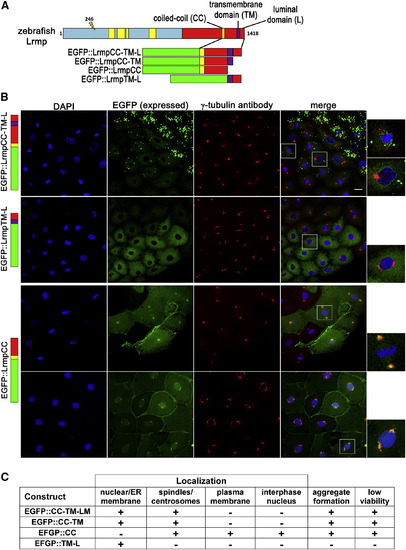
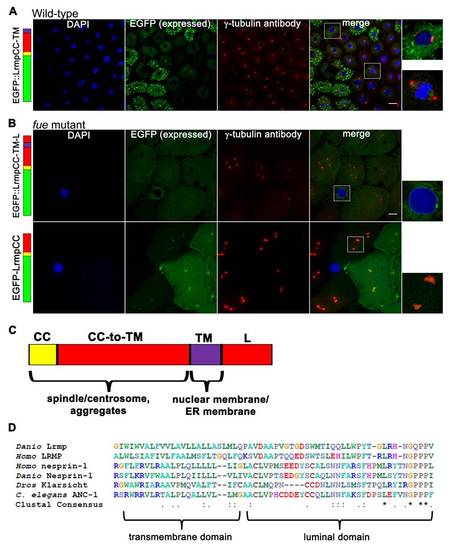
C-Terminal Domains of Lrmp Facilitate Subcellular Targeting (A) Diagram of EFGP-fusion constructs. (B) Fusion construct RNAs encoding EGFP::LrmpCC-TM-L (top row), EGFP::LrmpTM-L (second row), and EGFP::LrmpCC construct (bottom two rows) were injected into one-cell WT embryos. Embryos expressing EGFP were fixed and processed for DAPI and anti-γ-tubulin immunostaining between 2.5 and 3.5 hpf. White boxes indicate fields shown at higher magnification (right). Scale bar represents 20 μm in all lower magnification panels. (C) Summary of results from EGFP::Lrmp C-terminal protein expression. Low viability (far right column) manifested as cell division defects and failure to undergo gastrulation, which led to embryo lysis. See also Figure S5. |
|
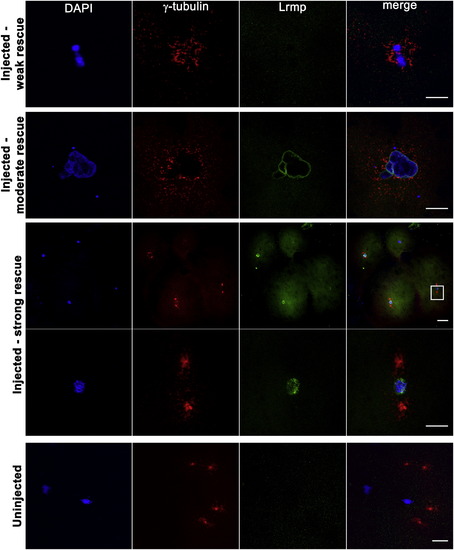
Mutant Oocyte Injection and Rescue with WT lrmp mRNA Stage IV oocytes from fue mutant females were isolated and injected with WT lrmp mRNA. Following maturation and in vitro fertilization, embryos were fixed at 1 hpf and labeled for DNA, γ-tubulin, and Lrmp. Examples of weakly rescued embryos (top row), moderately rescued embryos (second row), and strongly rescued embryos (third and fourth rows) are shown. White box in the third row indicates the region shown at higher magnification in the fourth row. Embryos from uninjected fue oocytes, derived from the same set of mothers and treated in parallel with injected oocytes, showed the typical mutant phenotype (bottom row). Scale bars represent 20 μm. See also Table S2. |
|
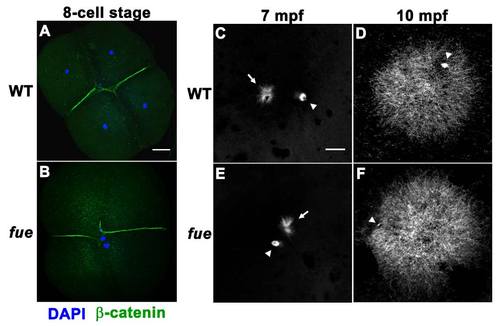
fue Embryos Fail to Undergo Pronuclear Migration and Fusion although the Sperm Aster Is Intact, Related to Figure 1 (A) DAPI (blue) and β-catenin (green) immunolabeling of wild-type embryos at the 4-cell stage. |
|
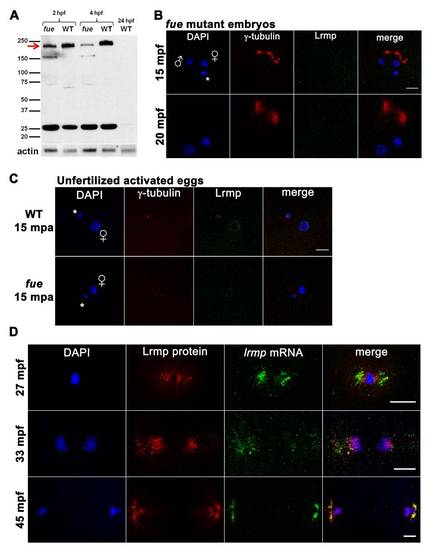
Western Blotting and Additional Protein/RNA Localization Analysis, Related to Figure 4 (A) Embryo lysates from wild-type and two fue mutant clutches at cleavage stages and 4 hpf were probed with anti-LrmpMD antibody. A band at 200 kDa (red arrow) likely corresponds to Lrmp and appeared reduced in mutant compared to wild-type, while a shorter 160 kDa band was present in mutant lysates. The observed 200 kDa molecular weight is greater than predicted for the zebrafish Lrmp isoforms (approximately 159 kDa - 162 kDa), however mouse and human Lrmp proteins also exhibit higher-than-expected molecular weights on denaturing gels (predicted at 62 kDa and 59 kDa, observed at 75 kDa and 69 kDa, respectively) [11,44]. The identity of the 25 kDa band seen in both mutant and wild-type is not known and unlike the 200 kDa species, was not recognized by the more C-terminal Lrmp antibody (data not shown). Wild-type 24 hpf lysates did not show any prominent signal. Anti-actin antibody was used as a loading control. |
|
Additional Observations on Fusion Protein Localization and Alignment of the Lrmp C-Terminal Domain to Known KASH Proteins, Related to Figure 5 (A-B) Embryos injected with fusion construct RNAs at the 1-cell stage were fixed at 2.5-3.5 hpf, then labeled with DAPI and anti-γ-tubulin antibody. |