- Title
-
Molecular dissection of the migrating posterior lateral line primordium during early development in zebrafish
- Authors
- Gallardo, V.E., Liang, J., Behra, M., Elkahloun, A., Villablanca, E.J., Russo, V., Allende, M.L., and Burgess, S.M.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
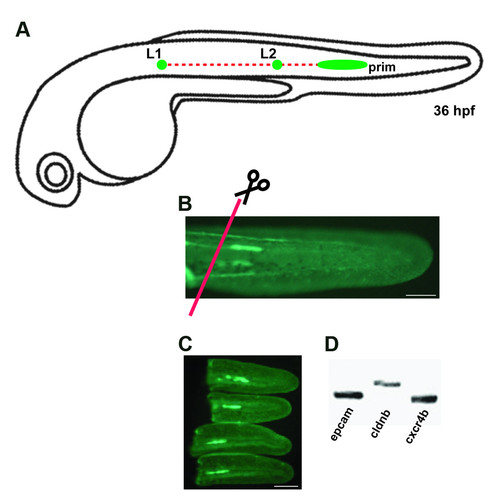
Section of the transgenic line cldnb:gfp. (A) Schematic drawings of a migrating primordium of the posterior lateral line along the horizontal myoseptum at 36 hpf. (B) Transgenic cldnb:gfp embryo at 36 hpf, when tails were sectioned (red line). (C) Sectioned tails with GFP primordium. (d) RT-PCR of RNA derived from dissected tails of 36 hpf embryos with primer specific to three genes known to be expressed in the primordium at this stage. L1: neuromast 1, L2: neuromast 2, prim: LLP primordium. Scale bars are 50 μm in (b-c). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
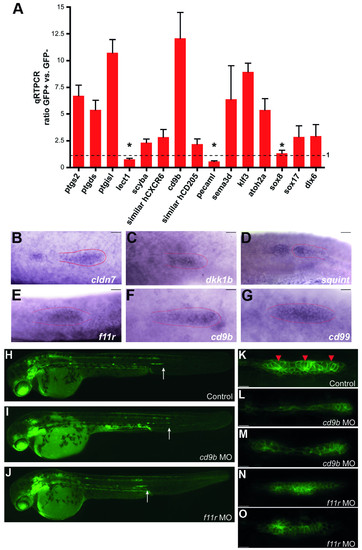
Validation of microarray analysis. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR for individual genes with different biological roles was performed of RNA derived from GFP+ and GFP- cells from tails of 36 hpf embryos. Real time PCR ratios were determined by normalization to β-actin (equal to 1, dotted line). Only 3 genes out of the 15 tested were not significantly enriched (asterisks). (B-G) In situ hybridization of 6 genes enriched in GFP+ cells showing a primordium specific expression pattern in 36 hpf embryos. (H-O) Loss-of-function analysis on two selected genes (cd9b and f11r) enriched in GFP+ cells of 36 hpf embryos. Cldnb:gfp embryos were injected with anti-sense morpholinos (MO) against cd9b (I, L-M) and f11r (J, N-O), and compared to control (H, K). White arrows indicate the position where the primordium is at 36 hpf (H-J). Red arrowheads indicate the rosette-like structures in the primordium (K). Scale bars are 10 μm in (B-G) and (K-O). |
|
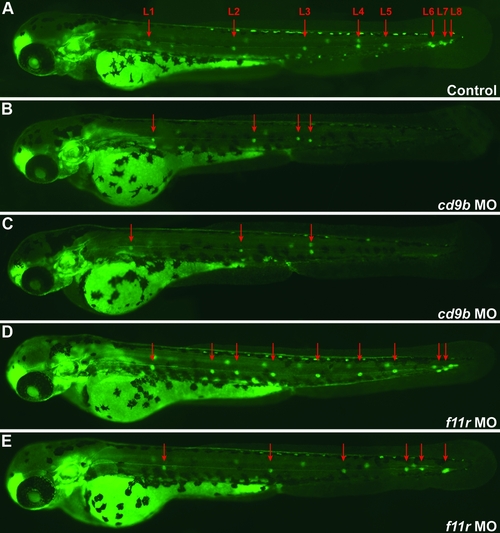
Pattern of the neuromast deposition in the embryonic PLL. The number and position of the neuromasts was analyzed in control (A), cd9bMO (B-C), and f11rMO (D-E) embryos at 48 hpf. Red arrows indicate the position of the PLL neuromasts. PHENOTYPE:
|