- Title
-
Visualization of embryonic lymphangiogenesis advances the use of the zebrafish model for research in cancer and lymphatic pathologies
- Authors
- Flores, M.V., Hall, C.J., Crosier, K.E., and Crosier, P.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
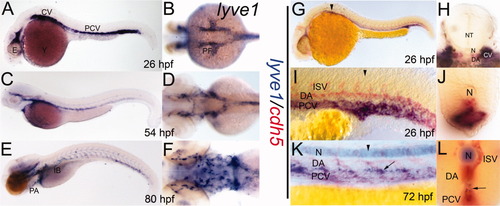
A-F: lyve1 riboprobe labeled developing lymphatic endothelial cells in 26 (A,B), 54 (C,D), and 80 (E,F) hours postfertilization (hpf) embryos (A,C,E, lateral view; B,D,F, dorsal view of anterior aspect). G-L: Double staining with lyve1 (blue) and cdh5 (red) riboprobes. G-J at 26 hpf; K,L at 72 hpf; G,I,K lateral views; H,J,L transverse sections approximately at the level of black arrowheads. K,L: The lyve1 expression within the developing thoracic duct (arrows). Background label within the notochord (N) due to extended staining time. CV, cardinal vein; DA, dorsal aorta; E, eye; IB, intestinal bulb; ISV, intersegmental vessels, NT, neural tube; PF, pectoral fin bud; PA, pharyngeal arches; PCV, posterior cardinal vein; Y, yolk. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
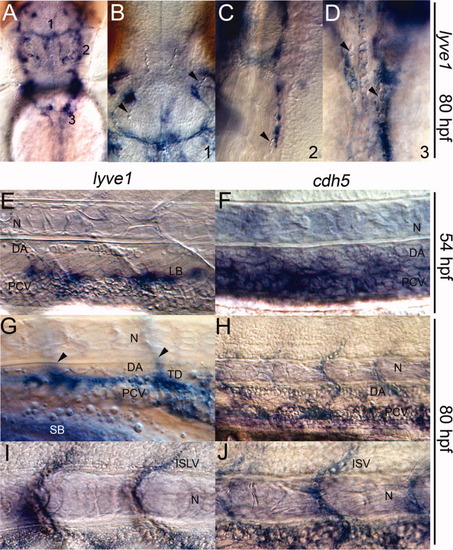
Vessels expressing lyve1 do not support circulating blood. A-J: Nomarski image of the head; dorsal view (A-D) and trunk, lateral view (E-J). B,C,D: lyve1-expressing structures within the head do not contain erythrocytes (arrowheads). E,F: At 54 hours postfertilization (hpf): lymphangioblasts (LB) expressing lyve1 lay just above the blood-filled posterior cardinal vein (PCV) in E; cdh5 marked both the dorsal aorta (DA) and PCV in F. G-J: At 80 hpf: lyve1 expression within the developing thoracic duct (TD) and intersegmental lymphatic vessels (arrowheads, out of focus) in G; lyve1 marked intersegmental lymphatic vessels (ISLV) in I; cdh5 marked the blood-filled DA, PCV and intersegmental vessels (ISV) in H and J; N, notochord. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
A-M: Presumptive lymph sacs (LS) in transverse sections through pectoral fin bud region and trunk in 26 hours postfertilization (hpf) and 48 hpf embryos. cdh5 expression in 26 hpf (A-C), 48 hpf (G-J). lyve1 expression in 26 hpf (D-F), 48 hpf (G,K-M). LS expressing lyve1 in 26 hpf embryos (asterisks) were adjacent to the cardinal vein (CV) in the pectoral region, while in the trunk, lyve1 still labeled the posterior cardinal vein (PCV). Dorsal views at 48 hpf showed distinct lyve1 and cdh5 expression patterns within the whole embryo. Expression of lyve1 within the PCV appeared diminished and had become prominent within the inter-axial vessel space (arrow). PF, pectoral fin buds; N, notochord; NT, neural tube; arrowheads in G mark the positions of the pectoral fins. |
|
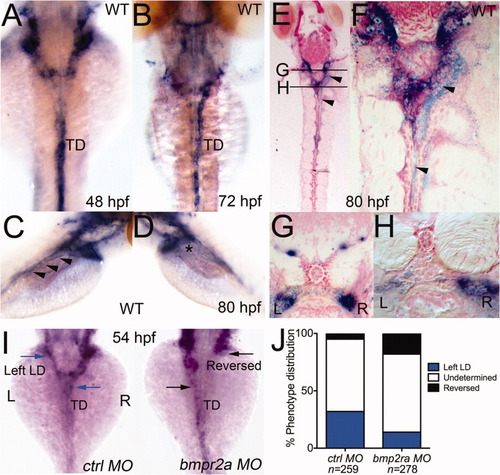
Zebrafish embryos develop asymmetric lymphatic collecting ducts. A,B: Dorsal views, lyve1 expression within lymphatic trunks of 48 and 72 hours postfertilization (hpf) embryos. C,D: Dorsolateral views, lyve1 expression within lymphatic trunks of 80 hpf embryos. Expression of lyve1 within the thoracic duct (TD) of an 80 hpf larvae visible from the right side of the larva (arrowheads), but discontinuous from the jugular lymphatics to the TD on the left side (asterisk). E-H: Coronal (E,F) and transverse (G,H) sections confirmed the laterality of the collecting ducts (relative positions marked in top middle panel). I,J: Depletion of a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor, Bmpr2a resulted in reversal of the LR architecture of lymphatic ducts in 54 hpf embryos. Dorsal views of 54 hpf embryos (I); graph of morphant phenotype distribution (J). Blue arrows and bars denote normal lymphatic duct asymmetry; Black arrows and bars denote reversed lymphatic duct (LD) asymmetry. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
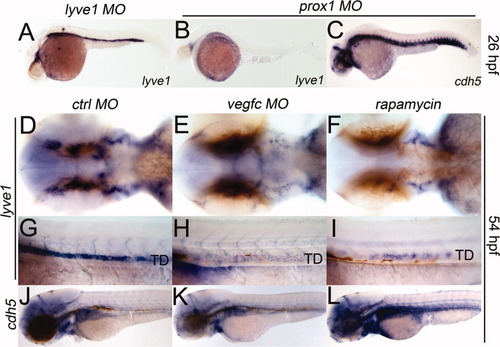
Effects of chemicals on lymphangiogenesis can be examined by monitoring expression of lyve1. A-C: Specification of lymphatic progenitors was not affected by lyve1 MO (A), but by prox1 MO (B,C), in 26 hpf embryos; blood vessel formation was unaltered (C). D-I: vegfc MO or 400 nM rapamycin reduced lymphatic budding and sprouting in 54 hpf embryos. J-L: Blood vessels remained normal in control and test embryos. All lateral views, except for D-F, which are dorsal views. TD, thoracic duct. |