- Title
-
Characterization of the neuroligin gene family expression and evolution in zebrafish
- Authors
- Rissone, A., Sangiorgio, L., Monopoli, M., Beltrame, M., Zucchi, I., Bussolino, F., Arese, M., and Cotelli, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
Analysis of zebrafish Neuroligins splicing pattern during embryo development and in adult organs. RT-PCR products were generated from total RNA extracted from different adult organs, oocytes, and stages of embryonic development. Specific beta actin primers (Argenton et al., [2004]) were used to check cDNA quality and possible genomic contamination. SS1 and SS2 indicate alternatively spliced sites of Neuroligin genes (Site A and Site B, respectively). Numbers on the left indicate the dimension in base pairs of the different molecular weights (MW). Control RT-PCR reactions without cDNA template were negative (data not shown). |
|
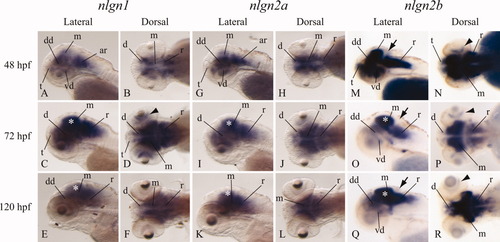
Temporal and spatial expression patterns of nlgn1, nlgn2a, and nlgn2b. Whole mount in situ hybridization assays were performed on embryos at 48, 72, and 120 hr post-fertilization (hpf). A-F: nlgn1 is mainly expressed in midbrain, hindbrain, and also in discrete regions of the diencephalon. At 72 hpf, a strong signal is visible throughout the whole brain. G-L: The expression of nlgn2a mRNA is similar to nlgn1. M-R: nlgn2b is widely detected at stage 48 hpf in the brain (with the exception of cerebellum, black arrows), and, unlike nlgn2a, in the retina (black arrowheads). From 72 hpf, the signal is detectable mainly in midbrain (especially in the tectum opticum, white asterisks), hindbrain, and discrete regions of the forebrain. Embryos are mounted with anterior to the left and dorsal up. ar, anterior rhomboencephalon; d, diencephalon; dd, dorsal diencephalon; m, mesencephalon; r, rhomboencephalon; t, telencephalon; vd, ventral diencephalon. |
|
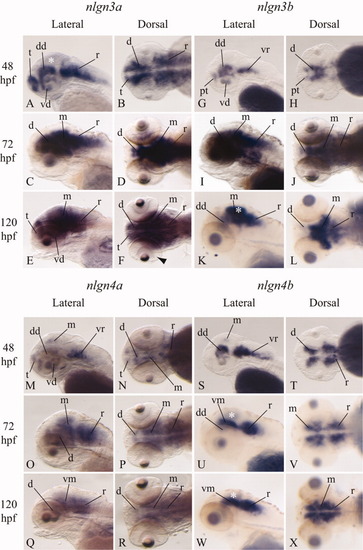
Analysis of Neuroligin 3a, 3b, 4a, and 4b expression patterns. In situ hybridization staining in 48-, 72-, and 120-hr post-fertilization (hpf) zebrafish embryos. A-F: nlgn3a mRNA is detected at 48 hpf in discrete regions of the telencephalon, dorsal and ventral diencephalon and rhomboencephalon, but no signal is present in the tectum opticum (white asterisks). At later stages, a widespread staining is visible in the brain, with the exception of the telencephalon at 72 hpf. G-L: At 48 hpf, nlgn3b mRNA is detectable in the posterior telencephalon, dorsal and ventral diencephalon, and the ventral portion of the rhomboencephalon. At 72 hpf, a widespread staining is visible in the brain, except for the telencephalon. At 120 hpf, the expression is restricted to the dorsal part of the diencephalon, to the midbrain (especially in the tectum opticum, white asterisk) and the anterior hindbrain. M-R: nlgn4a mRNA is weakly detectable at 48 hpf in discrete regions of brain. From 72 hpf onwards, its expression covers midbrain and the rostral hindbrain, with a faint signal in diencephalon. S-X: At 48 hpf, nlgn4b mRNA is strongly detectable in the dorsal diencephalon and ventral rhomboencephalon. From 72 hpf, a strong signal is present in the ventral mesencephalon and anterior rhomboencephalon. A very weak signal is also visible in the optic tectum (white asterisks) in every stage analyzed. Embryos are mounted with anterior to the left and dorsal up. d, diencephalon; dd, dorsal diencephalon; m, mesencephalon; pt, posterior telencephalon; r, rhomboencephalon; t, telencephalon; vd, ventral diencephalon; vm, ventral mesencephalon; vr, ventral rhomboencephalon. |