- Title
-
Co-activation of hedgehog and AKT pathways promote tumorigenesis in zebrafish
- Authors
- Ju, B., Spitsbergen, J., Eden, C.J., Taylor, M.R., and Chen, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol. Cancer
|
Expression of zebrafish Smoa1 activated the Hh pathway. A, whole-mount in situ hybridization of a control 12 hpf embryo showing ptc1 expression in adaxial structures. B, a 12 hpf transgenic embryo expressing CMV-smoa1-EGFP showed ectopic expression of ptc1 (Arrows). Scale bars, 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Zebrafish tumors induced by co-expression of zebrafish Smoa1 and constitutively active human AKT1. A, B and C, a 12-week-old fish with rhabdomyoma (A), showing GFP expression exclusively in the tumor (B); D, E and F, a 6-week-old fish with glioblastoma; G, H and I, a 8-week-old double transgenic fish with astrocytoma in the lower trunk region. Scale bars, 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Elevated phospho-AKT1 and Patched 1 levels in zebrafish tumors. A, B, a 3-week-old transgenic fish with trunk tumor (B) and its age-matched tumor-free fish (A). C, D, a 12-week-old fish with an eye tumor (D) and its age-matched tumor free fish (C). Immunofluorescence was done on cryosections for the above fish. E-H, an astrocytoma from a double transgenic fish showed elevated levels of both Patched 1 (F) and phosphorylated AKT (H). Immunofluoresence was done on paraffin sections for this tumor. Negative controls for Patched 1 (E) and phosphorylated AKT (G) were treated the same way except no primary antibodies were added. N, Notochord; AKT-P, phosphorylated AKT. Scale bars, 100 μm for A-D, 50 μm for E-H. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Overall strategy for co-expression of oncogenes in zebrafish. Stable transgenic lines expressing zebrafish Smoa1 were generated using a Tol2-based vector (A). Constitutively active human AKT1 (myrhAKT1) was incorporated into a meganuclease-based vector (B). The zebrafish krt4 promoter could simultaneously activate smoa1-EGFP and myrhAKT1 expression through Gal4VP16-UAS. |
|
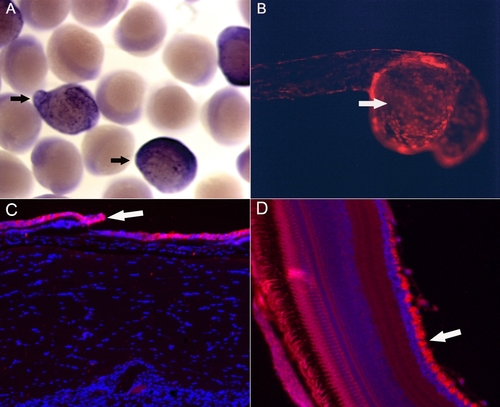
Expression patterns of transgenic line A. The data indicated that the cytokeratin 4 promoter drove epithelial cells-specific expression (arrows) of smoa1-EGFP as shown by in situ hybridization against EGFP in 12 hpf F1 embryos (A), and of tdTomato in a 24 hpf embryo generated by crossing the Tg(krt4:Gal4VP16;14 x UAS:smoa1-EGFP) and Tg(UAS:tdTomato) transgenic fish (B). At adult stage, GFP was detected predominantly in skin epithelial cells (C, arrow) and the retinal ganglion cells (D, arrow). |