- Title
-
A genetic screen in zebrafish identifies the mutants vps18, nf2 and foie gras as models of liver disease
- Authors
- Sadler, K.C., Amsterdam, A., Soroka, C., Boyer, J., and Hopkins, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
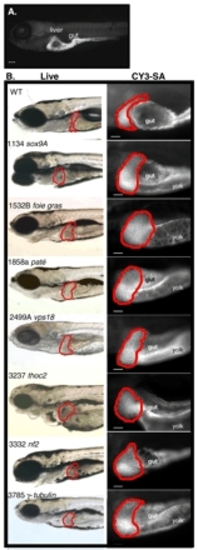
Seven mutants develop hepatomegaly by day 5 of development. (A) CY3-SA specifically labels the liver and gut in day 5 wild-type embryos. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B) Live images (left) and CY3-SA-labeled livers of wild-type and mutant embryos. The liver is outlined in red. The gut is indicated in each embryo, except fgr, which has an underdeveloped gut that does not label with CY3-SA. Scale bars: 50 µm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
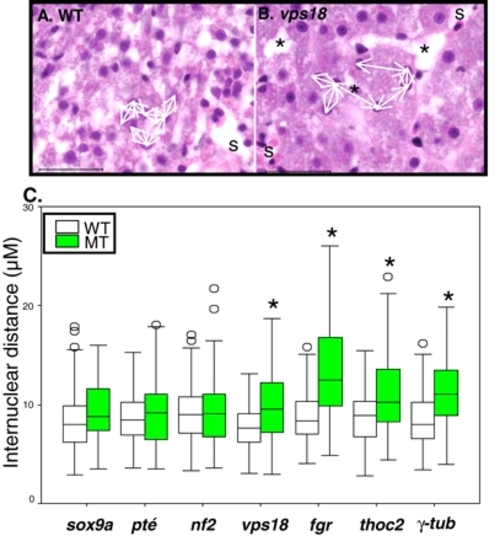
Four mutants with hepatomegaly have increased internuclear distance. (A,B) The internuclear distance between adjacent hepatocytes (white arrows) illustrated in wild-type (A) and vps18 (B) hepatocytes. Cells separated by sinusoids (s) or large extracellular gaps (*) were excluded. Scale bar: 50 µm. (C) The hepatocyte internuclear distance was measured for wild-type and mutant embryos from each line and plotted in box and whisker plots. The 25th, 50th (median) and 75th percentiles are indicated as the horizontal lines of the box, with the 10th and 90th percentiles shown as cross bars on lines extending from the boxes. Measurements falling outside of the 10th and 90th percent were considered outliers and are shown as open circles. *P<0.001, as determined by Student′s t-test.. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
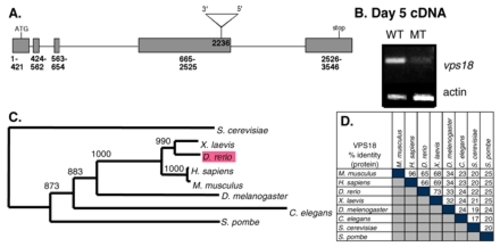
hi2499A mutants contain a mutagenic insertion in the vps18 gene. (A) Viral insertion in the vps18 gene at nucleotide 2236. Grey boxes indicate exons, horizontal lines indicate introns. Triangle represents virus. (B) cDNA prepared from day 5 phenotypically wild-type embryos and their mutant siblings from hi2499A was amplified with vps18 and actin primers. (C) Unrooted phylogenetic tree for vps18. Bootstrap numbers are indicated. (D) Percent identity matrix for the Vps18 protein. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
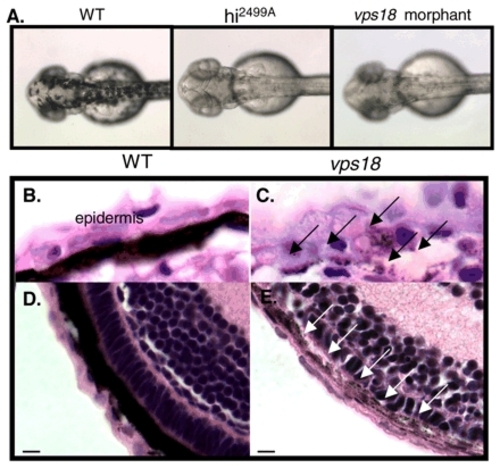
vps18 is required for pigment formation. (A) Day 2 hi2499A mutants and vps18 are not pigmented. (B-E) The day 5 epithelium of the skin (B,C) and the retina (D,E) is darkly pigmented in wild-type embryos (B,D), whereas vps18 mutants (C,E) have sparse pigment granules (arrows). Scale bar: 5 µm. |
|
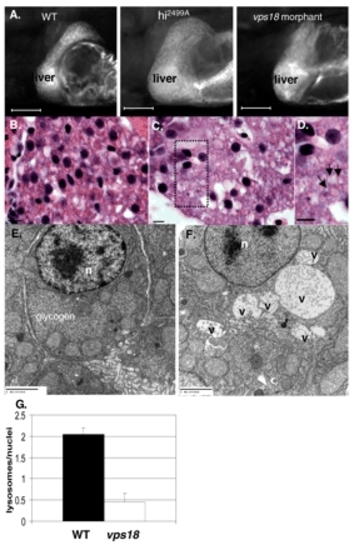
Mutation of vps18 results in vesicle accumulation and lysosome depletion in hepatocytes. (A) hi2499A mutants and vps18 morphants develop hepatomegaly. Scale bar: 100 µm. (B-D) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of day 5 wild-type (B) and vps18 mutant (C,D) livers. Hepatocytes in mutant embryos are large and accumulate vacuoles (arrows in D). Boxed area in C is enlarged in D. Scale bar: 5 µm. (E,F) TEM of day 5 wild-type (E) and vps18 (F) hepatocytes shows large, membrane-bound structures proteinacious material and debris, indicative of vacuoles (v) in the mutants. n, nucleus. (G) vps18 mutation reduces the number of lysosomes in hepatocytes. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
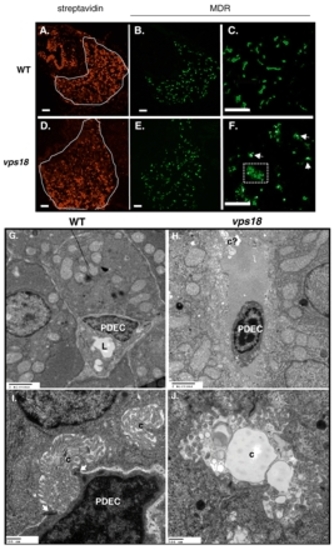
Mutation in vps18 results in biliary defects. (A-F) Confocal images of livers from wild-type (top) and vps18 mutant (bottom) embryos from day 5 (A,B,D,E) and day 7 (C,F) labeled with CY3-SA (A,D) and anti-MDR (B,C,E,F). Some hepatocytes in the mutant embryos retain some MDR in the cytoplasm (box in F). Scale bars: 10 µm. (G-I) TEM of day 5 embryos identifies PDECs as cells adjacent to hepatocytes that collect bile from the canaliculi of neighboring hepatocytes and transport it through their lumen (arrows in I). (H,J) vps18 mutant livers contain virtually no PDECs, and those that are found do not establish contacts with hepatocytes, are shrunken and have condensed DNA (H). PDEC, pre-ductal epithelial cell; c, canaliculi; c?, putative aberrant canaliculi; L, lumen. Scale bars: 20 µm G,H; 500 nm in I,J. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
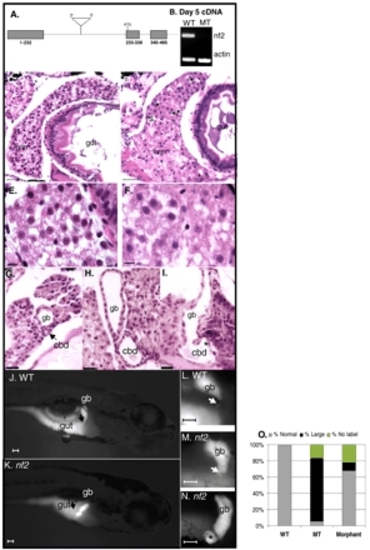
Mutation of the nf2 gene results in choledochal cyst formation. (A) hi3332 mutants contain an insertion in the intron upstream of the start site of the nf2 gene. Grey boxes indicate exons, lines indicate introns; ATG is the start codon. (B) cDNA prepared from day 5 phenotypically wild-type embryos and their mutant siblings from hi3332 was amplified nf2 and actin primers. (C-I) Hematoxylin and Eosin-stained histological sections through wild-type (D,E,G) and mutant (D,F,H,I) liver (C-F), gallbladder and common bile duct (G-I). Other than the large spaces in the mutant livers (asterisk in D), the wild-type and mutant livers appear similar (E,F). The common bile duct is cystic in nf2 mutant embryos (H,I). The section in I illustrates the gallbladder-ductal junction, and the formation of a diverticuli (asterisk) in the common bile duct of this embryo. Scale bars: 50 µm in C,D; 5 µm in E-I. (J-N) PED6 labeling of wild-type (J,L) and nf2 mutant (K,M,N) day 7 embryos. The gallbladder is a brightly labeled oblong or spherical organ in wild-type embryos, whereas it is always oblong in mutant embryos. The common bile duct (arrows) is dilated and diverticuli (asterisk in N) form in nf2 mutant embryos. (O) Quantification of ductal morphology in wild-type, mutant and nf2 morphant day 7 embryos fed PED6. P<0.003 for the comparison of the number of embryos with dilated bile ducts in wild-type and mutant embryos (not shown). Some mutant and morphant embryos do not accumulate any PED6 in their gallbladder (no label). gb, gallbladder; cbd, common bile duct. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
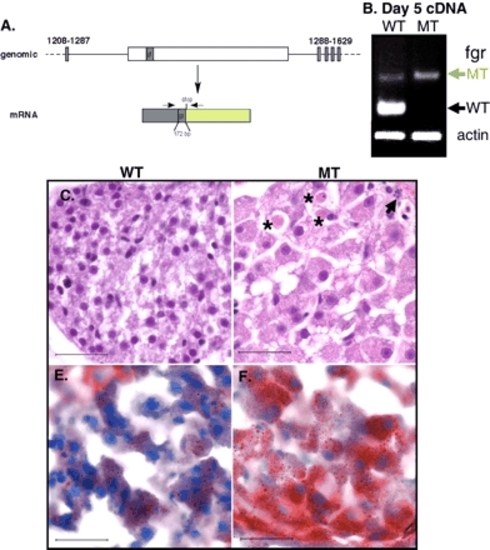
Mutation of fgr causes hepatomegaly and steatosis. (A) The viral insertion (white box) in the intron between exons 11 and 12 of the fgr gene in hi1532B mutants results in a gene trap cassette of 172 bp (gt, dark green) following bp 1286 of the fgr-coding sequence (grey box). The resulting transcript encodes a message that is frame shifted so that a stop codon is created following the gene trap sequence. (B) cDNA prepared from wild-type appearing embryos and their mutant siblings from a hi1532B was amplified with primers that span the trap (arrows on the mRNA diagram in A). As two-thirds of the wild-type appearing embryos from a hi1532B clutch are heterozygous for the mutant allele, both transcripts from the trapped allele (green arrow) in addition to transcripts the wild-type allele (black arrow) are amplified in these embryos. The mutant embryos only contain transcripts encoding the trap. Histology from wild-type (C) and mutant (D) day 5 embryos illustrates the large hepatocytes that are filled with vesicles. Several acidophilic bodies (asterisks) representing dead cells as well as those with condensed DNA and nuclear fragmentation (arrow) are evident in mutant livers, but are never observed in wild-type embryos. (E,F) ORO staining of wild-type (E) and mutant (F) livers from day 5 embryos reveals substantial steatosis in fgr mutant hepatocytes. Scale bar: 50 µm. |

Unillustrated author statements |