PUBLICATION
Zebrafish Regulatory T Cells Mediate Organ-Specific Regenerative Programs
- Authors
- Hui, S.P., Sheng, D.Z., Sugimoto, K., Gonzalez-Rajal, A., Nakagawa, S., Hesselson, D., Kikuchi, K.
- ID
- ZDB-PUB-171220-5
- Date
- 2017
- Source
- Developmental Cell 43: 659-672.e5 (Journal)
- Registered Authors
- Hesselson, Daniel, Hui, Subhra Prakash, Kikuchi, Kazu, Sheng, Delicia
- Keywords
- cardiomyocyte, heart, neural stem cell, regeneration, regulatory T cell, retina, spinal cord, zebrafish
- MeSH Terms
-
- Animals
- Cell Differentiation/physiology
- Cell Proliferation/physiology
- Forkhead Transcription Factors/physiology
- Heart/physiology
- PubMed
- 29257949 Full text @ Dev. Cell
Abstract
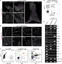
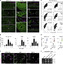
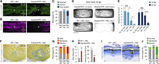
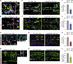
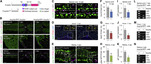
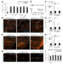
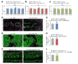
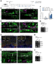
The attenuation of ancestral pro-regenerative pathways may explain why humans do not efficiently regenerate damaged organs. Vertebrate lineages that exhibit robust regeneration, including the teleost zebrafish, provide insights into the maintenance of adult regenerative capacity. Using established models of spinal cord, heart, and retina regeneration, we discovered that zebrafish Treg-like (zTreg) cells rapidly homed to damaged organs. Conditional ablation of zTreg cells blocked organ regeneration by impairing precursor cell proliferation. In addition to modulating inflammation, infiltrating zTreg cells stimulated regeneration through interleukin-10-independent secretion of organ-specific regenerative factors (Ntf3: spinal cord; Nrg1: heart; Igf1: retina). Recombinant regeneration factors rescued the regeneration defects associated with zTreg cell depletion, whereas Foxp3a-deficient zTreg cells infiltrated damaged organs but failed to express regenerative factors. Our data delineate organ-specific roles for Treg cells in maintaining pro-regenerative capacity that could potentially be harnessed for diverse regenerative therapies.
Genes / Markers
Expression
Phenotype
Mutations / Transgenics
Human Disease / Model
Sequence Targeting Reagents
Fish
Orthology
Engineered Foreign Genes
Mapping