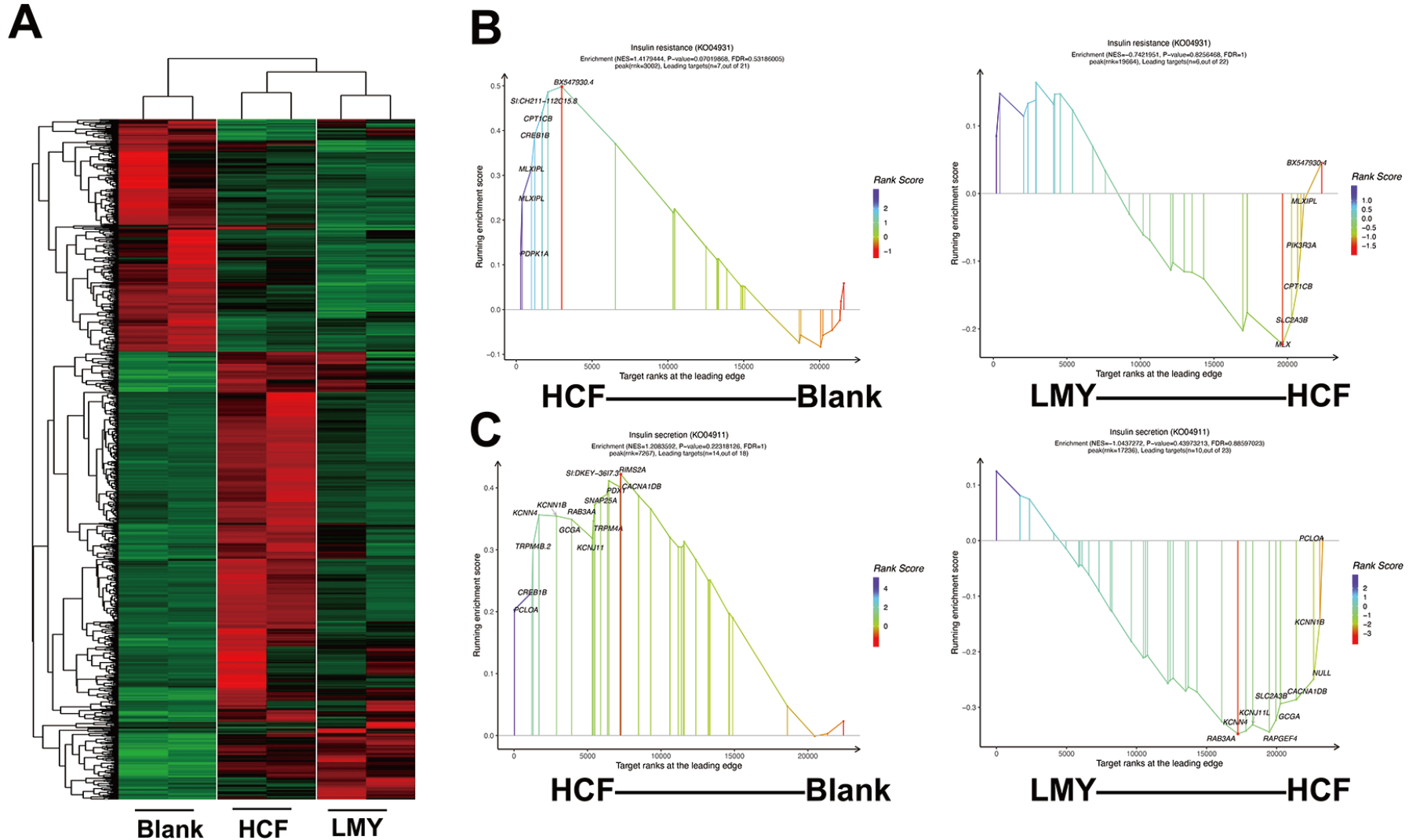
Fig. 3 LMY antagonizes the NAFLD-prone transcriptome induced by the HCF diet in zebrafish liver(A) Heatmaps represent the treatment groups’ DEGs. The adult zebrafish were first fed with the HCF diet for four weeks before being administered with LMY for another four weeks. The livers of the treated fish were then harvested for RNA-seq. (B) GSEA curve of the insulin resistance subset with plots of significantly-changed genes. (C) GSEA curve of the insulin secretion subset with significantly-changed genes. Considering that the KEGG analysis only demonstrates the difference between the two groups, we cannot obtain information on how the genes changed in an enriched pathway. Hence, GSEA was performed to analyze the RNA-seq data further. We found that the HCF diet particularly elevated insulin secretion and insulin resistance-related pathway activity in the zebrafish liver. These pathways were partially reversed by LMY treatment (Figure 3B,C), suggesting that the classical endocrine regulatory activity of LMY is similar to its clinical application.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Acta. Biochim. Biophys. Sin (Shanghai)