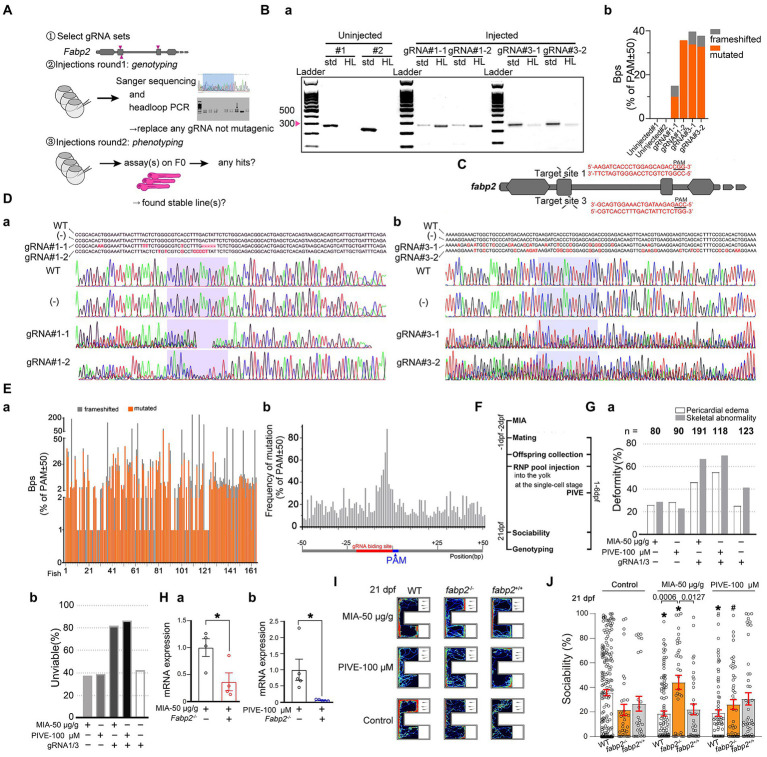
Figure 7
Fabp2 gene F0 knockout ameliorated MIA-induced autism-like behaviors. (A) Two rounds F0 knockout of fabp2 gene including selection of gRNAs, verification of mutagenic gRNAs and phenotyping. (Ba) Target loci of fabp2 amplified with the PCR primes used for sequencing (std, standard) or with headloop primer (HL). (Bb) Frameshifted and mutated bps (Sanger sequencing) of the same samples as showed in (Ba). (C) Schematic diagram of the target site in the zebrafish fabp2 genome. (Dab) Sequencing maps of WT and fabp2−/− zebrafish. (−): gRNA not mutagenic. (Ea) Frameshifted and mutated bps (Sanger sequencing) of all samples (83 fish at 21 dpf; 46 fish at 1 mpf which for finding stable lines). (Eb) Frequency of mutations of R50-PAM-F50 (83 fish at 21 dpf; 46 fish at 1 mpf which for finding stable lines). (F) After maternal poly(I:C) injection (MIA), two-RNP pool was injected into the yolk at the single-cell stage before cell inflation; or two-RNP pool was injected into the yolk at the single-cell stage followed by PIVE to these embryos, and zebrafish were tested for sociability at 21 dpf followed by verification of genotyping. (Ga) Deformity of gRNA injection with MIA or PIVE. (Gb) Unviability of gRNA injection with MIA or PIVE. (Hab) mRNA expressions of