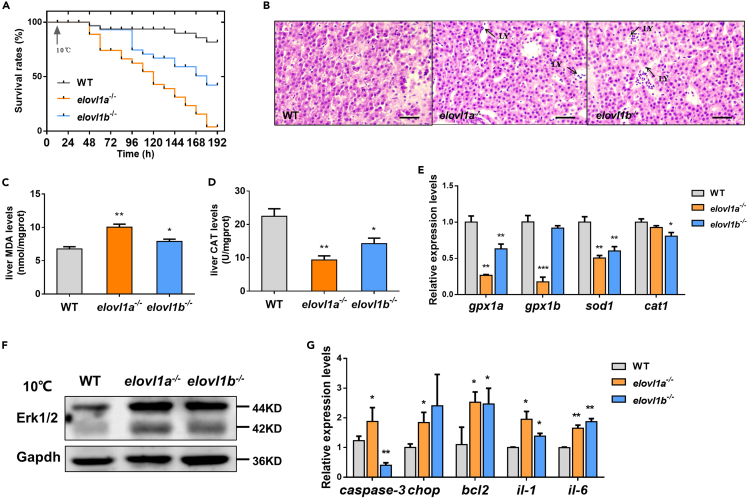
Fig. 3
Effects of elovl1a and elovl1b deletion on cold tolerance of zebrafish
(A) The survival rates of fish during cold stress.
(B) Histological structures of livers from WT, elovl1a–/–, and elovl1b–/– zebrafish under cold stress. Scale bar, 20 μm.
(C and D) The levels of MDA (C) and CAT (D) in livers of WT, elovl1a–/–, and elovl1b–/– zebrafish under cold stress (n = 5).
(E) Hepatic expression levels of four oxidative stress-related genes in WT, elovl1a–/–, and elovl1b–/– zebrafish under cold stress.
(F) Western blotting of Erk1/2 in livers of WT, elovl1a–/–, and elovl1b–/– zebrafish under cold stress.
(G) Hepatic expression levels of apoptosis and inflammation-related genes in WT, elovl1a–/–, and elovl1b–/– zebrafish under cold stress. Data were given as means ± SD of three biological replicates unless otherwise specified. The statistical analyses were conducted by t test. The asterisks labeled above the error bars indicated significant differences (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). WT, wild-type zebrafish; elovl1, fatty acyl elongase 1; elovl1a–/–, elovl1a knockout zebrafish; elovl1b–/–, elovl1b knockout zebrafish; LY, lymphocyte; MDA, malondialdehyde; CAT, catalase; gpx-1a, glutathione peroxidase 1a; sod1, superoxide dismutase 1, soluble; cat1, catalase 1; Erk1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2; Gapdh, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; chop, DNA damage inducible transcript 3; bcl2, BCL2 apoptosis regulator a; il, interleukin.