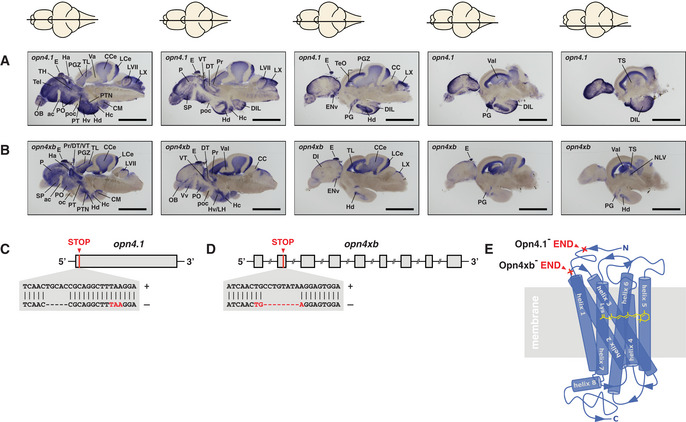
Figure 1 melanopsin expression in the brain and knockout strategy
A, B In situs on adult brain sections reveal that (A) opn4.1 and (B) opn4xb are coexpressed in many brain domains including the epiphysis cerebri (indicated with E) or pineal. A horizontal line through a representation of the brain, above the section, indicates the location of the section within the brain. Scale bar: 1.0 mm. The brain domains in which the five melanopsins are expressed are presented in Fig EV1 and Table EV1.
C The TALEN genome‐editing technique was applied for site‐directed mutagenesis. A 5 bp deletion was introduced proximal to the start codon of
D An 8 bp deletion was introduced in the second exon (grey box) of the opn4xb gene resulting in a premature stop codon.
E Model of the seven transmembrane G‐protein‐coupled photoreceptor shows the light absorbing molecule, the chromophore retinal (yellow), bound to helix 7 (blue). The red crosses indicate where the Melanopsins in the mutants are truncated: the mutated Opn4.1 has lost all transmembrane helices and the mutated Opn4xb ends after the second transmembrane helix. From the structure–function relationship of the photoreceptor, one can deduce that neither of the mutant Melanopsins is functional.