Fig. 9
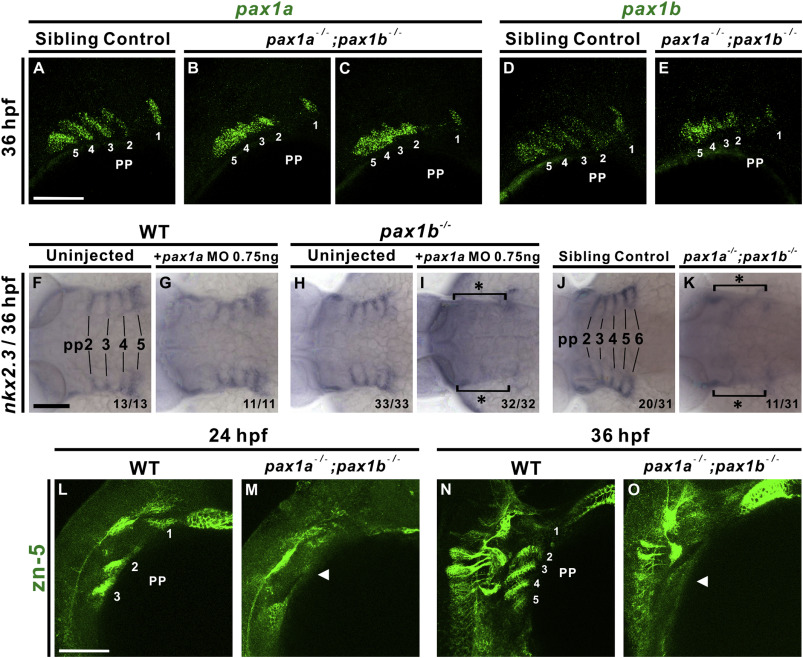
Fig. 9 pax1a- and pax1b-deficient embryos exhibit morphogenetic defects and lack of nkx2.3 or Alcama expression in pharyngeal pouches. Segmented pharyngeal pouch (pp) 1 expresses pax1a or pax1b, while unsegmented pharyngeal pouches 2–5 display continuous expression of pax1a or pax1b and small outpocketings in pax1a−/−; pax1b−/− double mutant embryos (B, C, E); sibling controls (i.e., pax1a+/−; pax1b−/− or pax1a+/+; pax1b−/−) show normal segmentation (A, D) when hybridized with pax1a or pax1b RNA probes at 36 hpf. Absent expression of nkx2.3 in the pharyngeal pouches (pp) 2–5 was observed in 0.75 ng pax1a MO-injected pax1b−/− mutant embryos (I) compared to un-injected pax1b−/− mutants (H), wild types (WT; F) or 0.75 ng pax1a MO-injected wild types (G) at 36 hpf. A similar defect in nkx2.3 expression in pharyngeal pouches 2–6 was also identified in pax1a−/−; pax1b−/− double mutants (K) compared with sibling controls (i.e., pax1a+/−; pax1b−/− or pax1a+/+; pax1b−/−) (J). A lack of Alcama expression (arrowhead; labeled by anti-zn5 antibody) was noted in the pharyngeal pouches of pax1a−/−; pax1b−/− double mutants in contrast with wild types at 24 hpf (L, M) and 36 hpf (N, O). Scale bars represent 100 μm.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 161, Liu, Y.H., Lin, T.C., Hwang, S.L., Zebrafish Pax1a and Pax1b are required for pharyngeal pouch morphogenesis and ceratobranchial cartilage development, 103598, Copyright (2020) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.