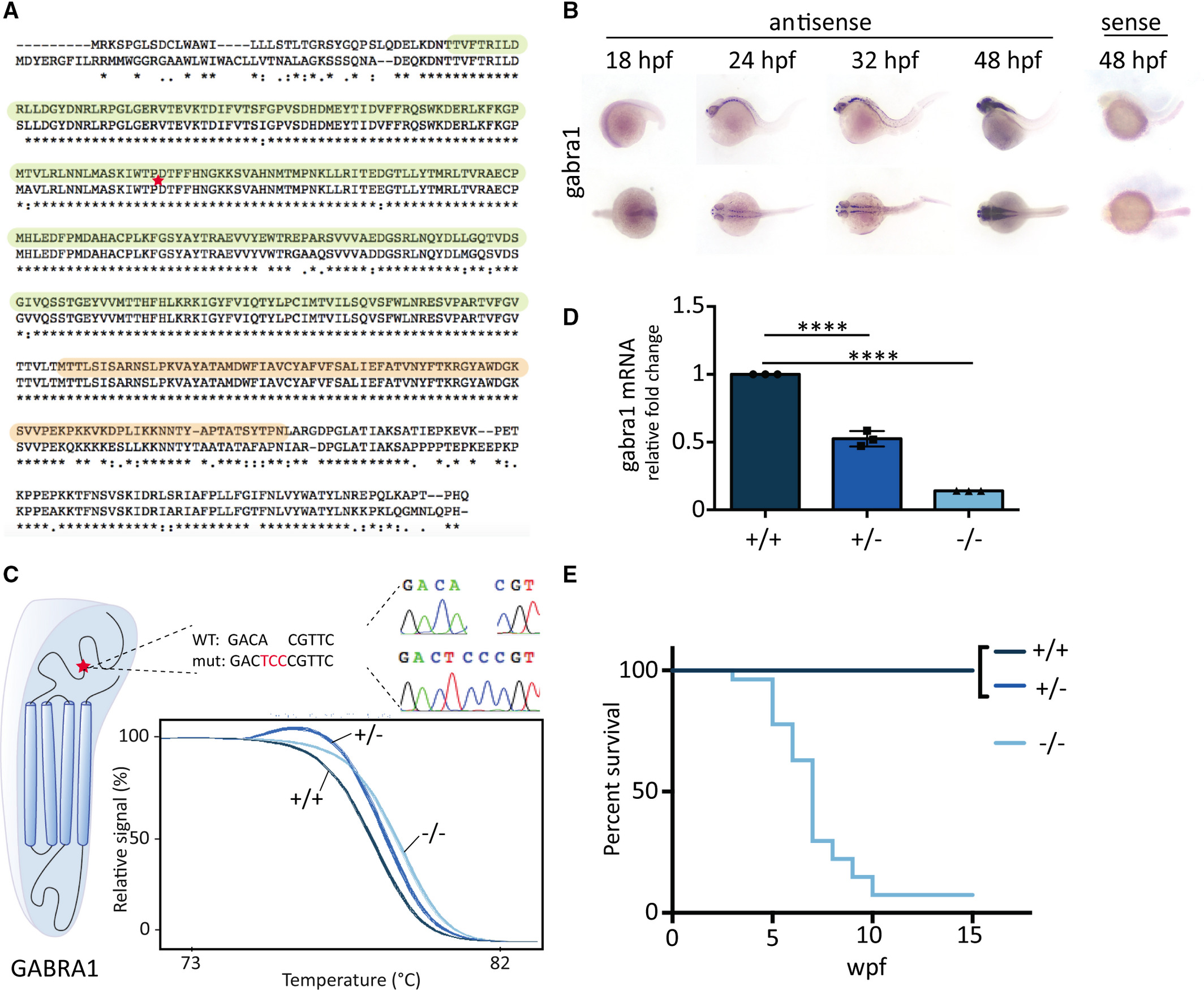
Fig. 1 GABRA1 knockout leads to premature death in zebrafish. A, Human (top, ENST00000393943.9) and zebrafish (ENSDART00000100000.4) GABRA1 protein sequences were aligned using Clustal W algorithm, and amino acid identity is indicated by asterisks. Colons and dots indicate conservation between amino acid of strongly or weakly similar properties, respectively. The γ‐aminobutyric acid (GABA) binding and transmembrane domains are highlighted in green and orange, respectively. The CRISPR‐targeted site is indicated with a red star. B, Whole mount in situ hybridization against gabra1 mRNA showed a faint expression in the central nervous system at 18 hours postfertilization (hpf) that increased in the developing brain at 24 and 32 hpf. The expression was broad, strong, and restricted to the brain at 48 hpf. C, CRISPR mutagenesis of the GABRA1 GABA‐binding domain coding sequence led to the A>T+CC mutation (mut). The mutation was confirmed by Sanger sequencing. WT, wild‐type. D, Real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of RNAs from 5 days postfertilization larvae (in triplicate with n = 7) shows a significant decrease of gabra1 mRNA expression in gabra1+/− (52.52% of WT ± 0.0327) and gabra1−/− (14.04% of WT ± 0.00058) larvae when compared to their WT siblings (one‐way analysis of variance and Tukey multiple comparison test; ****P < 0.0001). E, The progeny of gabra1+/− individuals was genotyped by tail‐clipping at 1 week postfertilization (wpf), raised separately according to their genotypes, and the survival of each class (+/+, +/−, −/−; n = 8) was monitored every week until 15 weeks of age.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Epilepsia