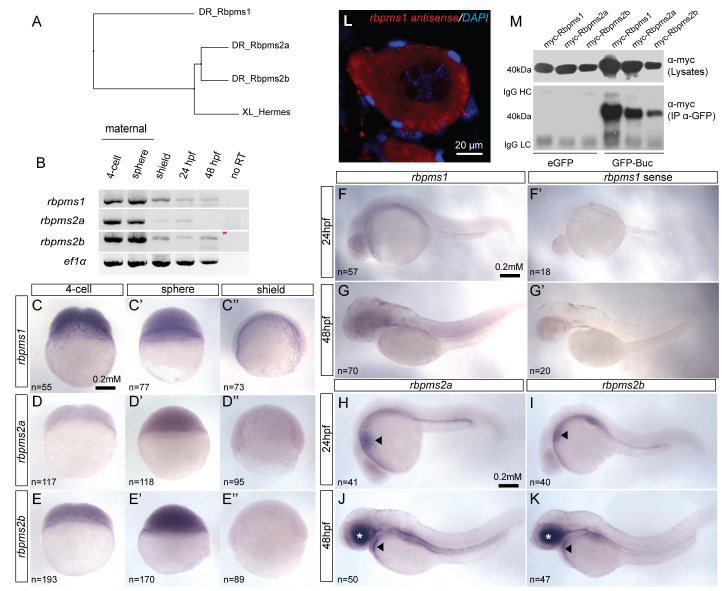
Fig. S1
Conserved expression of Xhermes homologs in zebrafish.
(A) Phylogenetic tree clustered according to protein sequence similarity between Xenopus Hermes and zebrafish Hermes homologs Rbpms1, Rbpms2a, and Rbpms2b. (B) RT-PCR on maternal and zygotic stages of zebrafish embryonic development demonstrate all three RNAs are abundant as maternal transcripts. (CE’’) Lateral views of whole-mount in situ hybridization (ISH) for rbpms1, rbpms2a and rbpms2b in 4-cell, sphere, and shield- stage embryos. Lateral views of 24 hpf ISH for rbpms1 (F), and sense probe control (F’). Lateral views of 48 hpf ISH for rbpms1 (G), and sense probe control (G’). Lateral views of 24 hpf embryos shows similar rbpms2a (H) and rbpms2b (I) ISH staining in heart primordium (arrow heads). Lateral view of 48 hpf embryos reveals similar rbpms2a (J) and rbpms2b (K) ISH staining pattern in the heart (arrow head) and retina (white asterisk). (L) Fluorescent in situ hybridization displaying unlocalized rbpms1 transcripts in primary zebrafish oocyte. (M) GFP immunoprecipitation of Myc- tagged Rbpms1, Rbpms2a and Rbpms2b demonstrates that that all three proteins can interact with GFP-Bucky ball in vitro.