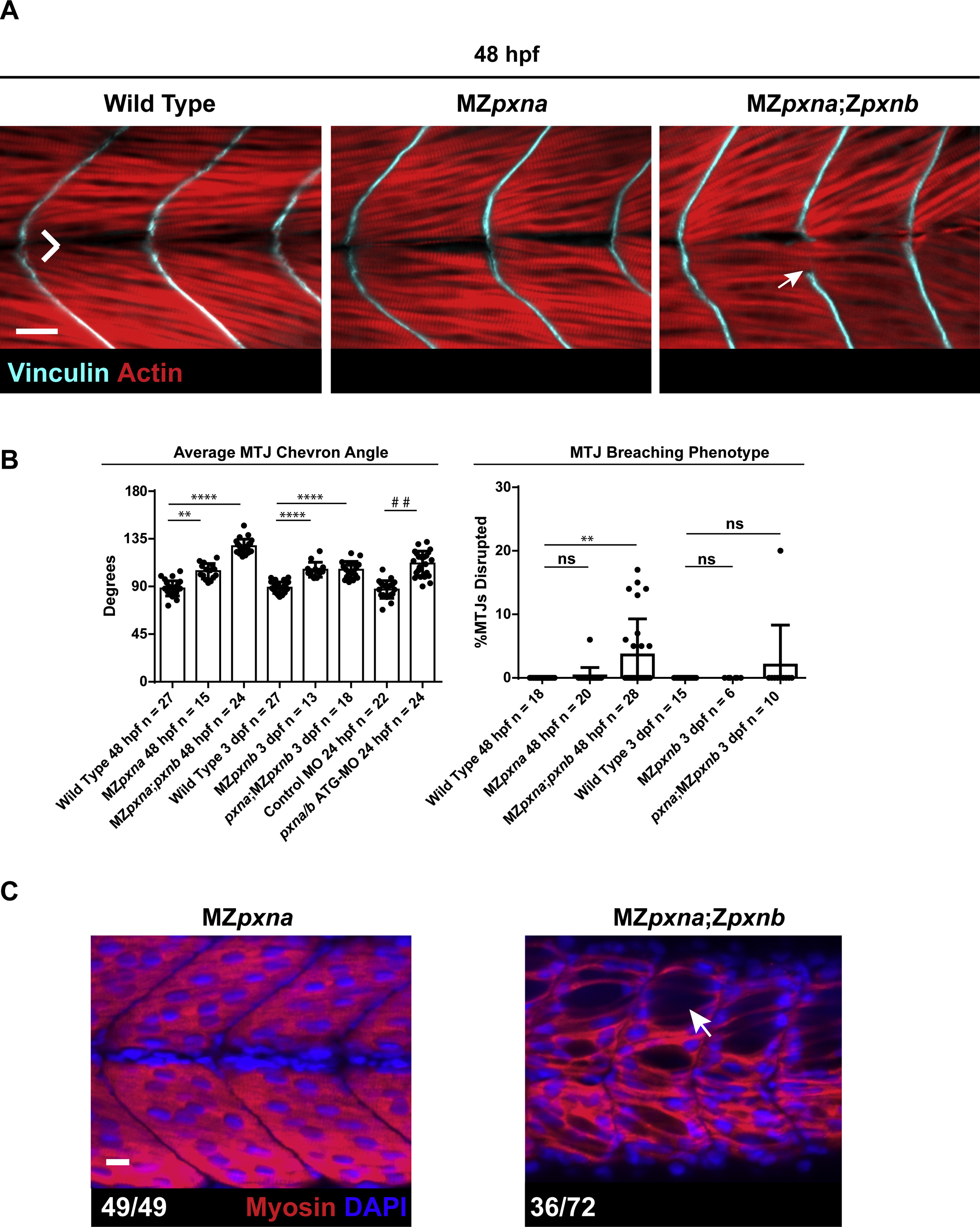
Fig. S2
Myotome and MTJ Defects Develop by 48 hpf in MZpxna;Zpxnb embryos. (A) Immunostaining for myofibers and MTJs at 48 hpf revealed that MZpxna;Zpxnb embryos exhibit large gaps and myoblast elongation through MTJs (white arrow). Scale bar =25 µm (B) Quantification of MTJ chevron angle and MTJ breaching revealed that MTJ defects arise by 48 hpf in Paxillin MZ single and double mutant embryos. Injection of the pxna/b ATG-MO also resulted in a wider MTJ chevron angle compared to control MO injected embryos at an earlier stage of development. Data points represent individual embryo means and error bars show standard deviations from three independent experiments. **** p<0.001, ** p<0.005 determined by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparisons post-hoc test, # # p<0.01 determined by T-test, ns = not significant. (C) Immunostaining for Myosin revealed that a substantial number of MZpxna;Zpxnb embryos had large gaps between myofibers (arrow). The number of embryos exhibiting depicted phenotypes over the total number of embryos examined for three independent experiments is shown. Scale bar =10 µm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 425(1), Jacob, A.E., Amack, J.D., Turner, C.E., Paxillin Genes and Actomyosin Contractility Regulate Myotome Morphogenesis in Zebrafish, 70-84, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.