Fig. 3
Fig. 3
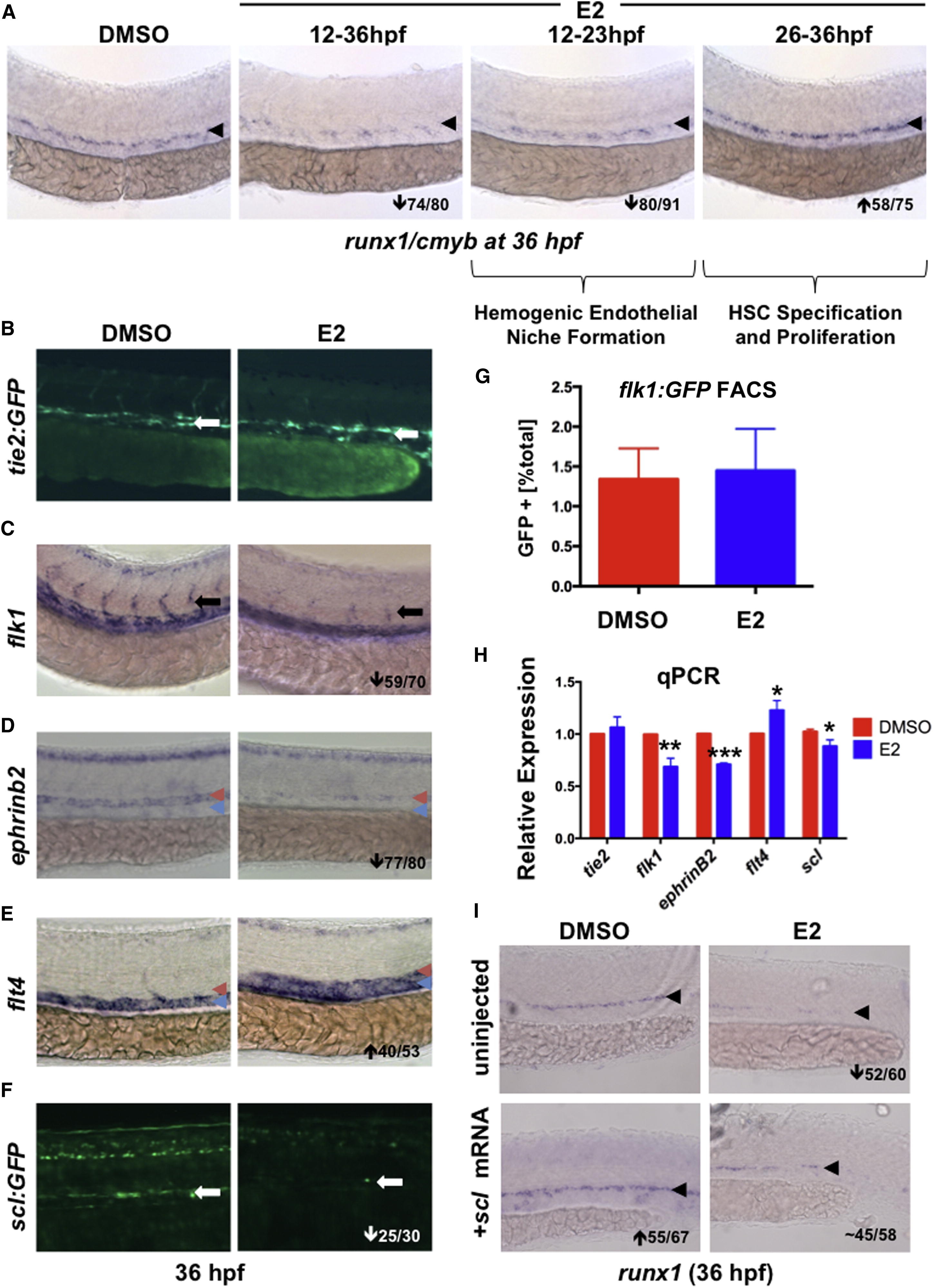
E2 Exposure Impairs Formation of the Hemogenic Endothelial Niche
(A) E2 had a biphasic effect on HSPCs: treatment during hemogenic niche specification (12–23 hpf) decreased runx1, whereas exposure during HSC specification and budding (26–36 hpf) increased HSPCs (n ≥ 75/treatment).
(B) Treatment with E2 had no impact on axial vessel formation as assessed by tie2:GFP (n ≥ 20).
(C) E2 disrupts ISV formation as indicated by flk1 WISH (59/70).
(D) Arterial ephrinb2 was robustly decreased by E2 (77/80); red arrowheads indicate artery, and blue arrowheads indicate vein.
(E) Venous flt4 was increased after E2 exposure (40/53).
(F) scl:GFP was reduced by E2 treatment (25/30).
(G) FACS of flk1:GFP+ embryos (n = 32) revealed no change in endothelial cell number by E2 (error bars indicate SD).
(H) qPCR confirmed decreased expression of flk1, ephrinB2, and scl following E2 treatment (mean of triplicate experiments ± SEM; one-tailed t test; flt4∗p < 0.05, flk1∗∗p < 0.01, and ephrinB2∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(I) Injection of scl mRNA increased runx1 expression in the AGM and rescued loss following E2 treatment (n > 55 per treatment).