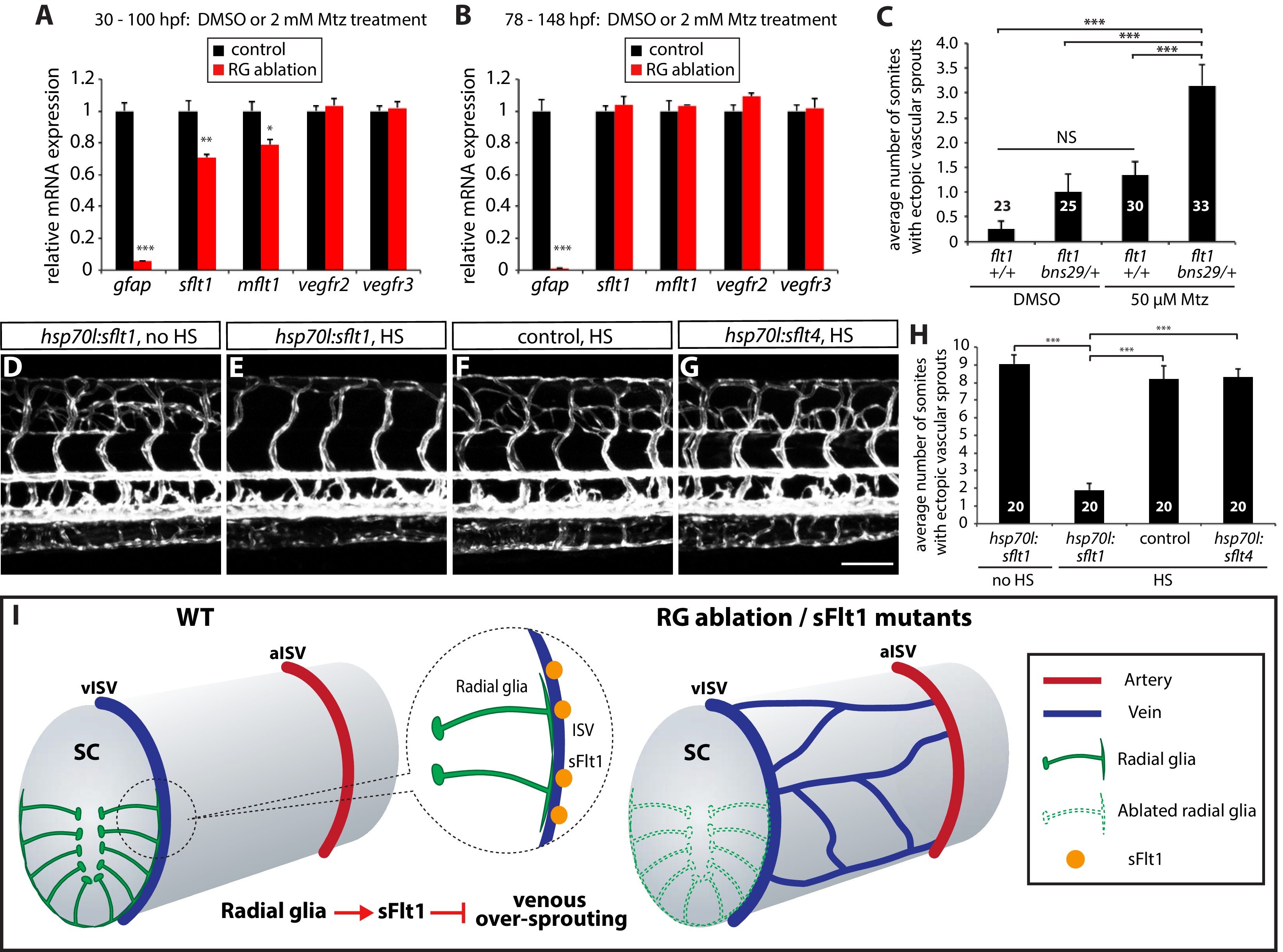
Fig. 7
Radial glia limit venous over-sprouting around the spinal cord via the regulation of sflt1 expression.
(A) qPCR analyses of 100 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk samples after treatment with DMSO or 2 mM Mtz between 30 and 100 hpf. Radial glia-ablated fish trunk samples show significantly reduced mRNA expression of gfap, sflt1, and mflt1. (B) qPCR analyses of 148 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk samples after treatment with DMSO or 2 mM Mtz between 78 and 148 hpf. Radial glia-ablated fish trunk samples show significantly reduced gfap mRNA expression; however, sflt1 and mflt1 mRNA expression was not significantly different between control and radial glia-ablated samples. (C) Quantification of average number of somites that showed ectopic sprouting in 154 hpf flt1+/+ and flt1bns29/+ larvae treated with DMSO or 50 µM Mtz between 30 and 154 hpf (10 somites examined per animal; ≥23 animals examined per condition). flt1+/+ larvae treated with 50 µM Mtz or flt1bns29/+ larvae treated with DMSO did not show a statistically significant change in ectopic ISV sprouting compared to flt1+/+ larvae treated with DMSO. However, flt1bns29/+ larvae treated with 50 µM Mtz exhibited a significantly increased number of somites with ectopic sprouts compared to the other three treatments. See also Figure 7—source data 1 for quantification. (D–G) 154 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR);Tg(kdrl:EGFP);Tg(hsp70l:sflt1, cryaa:cerulean) (D and E), TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR);Tg(kdrl:EGFP) (F), and TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR);Tg(kdrl:EGFP);Tg(hsp70l:sflt4, cryaa:cerulean) (G) trunk vasculature visualized by Tg(kdrl:EGFP) expression. Animals were treated with 2 mM Mtz between 30 and 54 hpf and then subject to no heat shock (D) or multiple heat shocks (E–G) starting at 62 hpf and every 12 hr after that. Overexpression of sFlt-1 blocks ectopic vessel sprouting after radial glia ablation (E). Scale bar, 100 µm. (H) Quantification of average number of somites that showed ectopic sprouting for the experiments shown in panels D–G (10 somites examined per animal; 20 animals examined per condition). Quantification was performed at 154 hpf. Overexpression of sFlt-1, but not of sFlt-4, significantly inhibited ectopic vessel sprouting after radial glia ablation. HS: heat shock. (I) Schematic diagrams showing radial glia regulation of the vascular patterning around the spinal cord. During development, the end-feet of radial glia lie in close proximity to the dorsal ISVs which surround the spinal cord. Genetic ablation of radial glia in early embryos leads to selective over-sprouting of venous ISVs. Perturbation of sFlt1 function also leads to over-sprouting of vISVs, and radial glia regulate the precise patterning of the venous vasculature around the spinal cord at least in part via the control of sFlt1 function in endothelium. RG: radial glia. In panels (C and H), values represent means ± SEM (*** indicates p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD test). In panels (A and B), values represent means ± SEM (*, **, and *** indicate p<0.05, p<0.01, and p<0.001, respectively, by Student’s t test).