Fig. 6
Loss of Fgf Signaling and HS Function Leads to Random, Dynamic Filopodia Formation
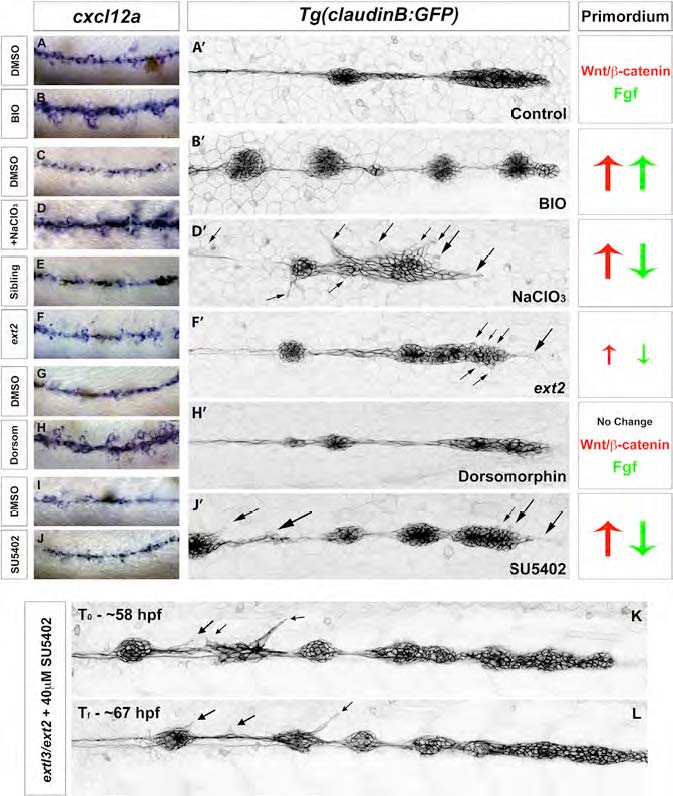
(A-B′) BIO-treated Tg(claudinB:GFP) embryos show upregulation of cxcl12a compared to control embryos, but no evidence of ectopic filopodia formation. BIO treatment leads to upregulation of the Wnt and Fgf pathways in the prim.
(C-D′) In NaClO3-treated Tg(claudinB:GFP) embryos where cxcl12a is upregulated. Filopodia form along all LL cells (D′). Similarly to extl3/ext2 mutants, these embryos show upregulation of Wnt and loss of Fgf signaling.
(E-F′) cxcl12a is only slightly upregulated in ext2 mutants. Mild ectopic filopodia are observed in the most anterior region of the prim by time-lapse recording (F′; Movie S3); 48 hpf ext2 mutants show only partial Wnt upregulation and Fgf signaling downregulation (data not shown).
(G-H′) Bmp signaling inhibition with Dorsomorphin leads to an increase in cxcl12a-expressing muscle cells. Bmp inhibition does not alter prim migration or signaling, but induces the upregulation of cxcl12a.
(I-J′) Inhibition of Fgf signaling by SU5402 causes the formation of ectopic filopodia, but not upregulation of cxcl12a (J′). Wnt is upregulated as a result of Fgf inhibition.
(K and L) Inhibition of Fgf signaling in extl3/ext2 mutants does not eliminate ectopic protrusions. Black arrows point to ectopic filopodia.
See also Figures S4 and S5 and Movies S6 and S8.