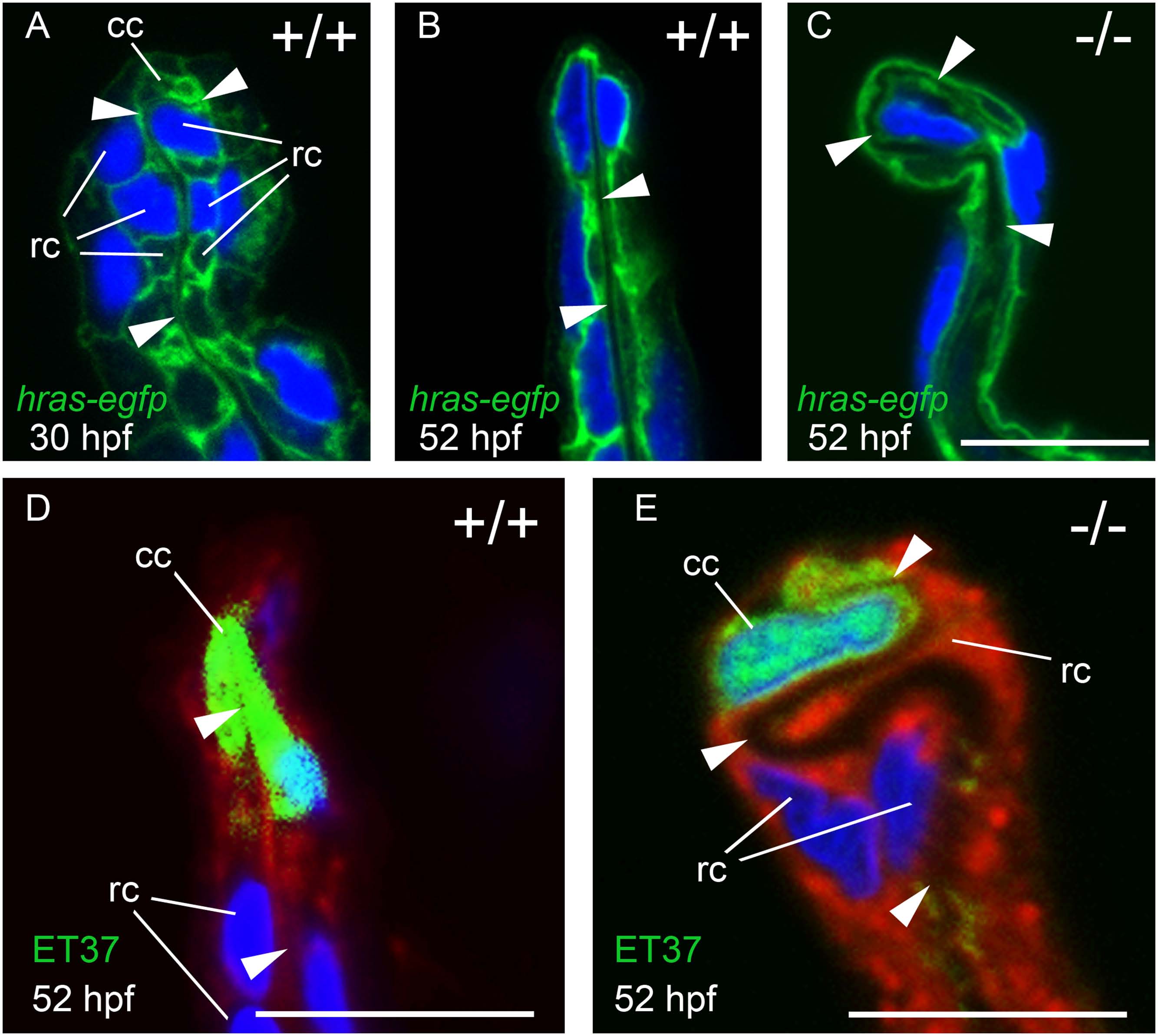
Fig. 7 MFF cleft cells of nrg2a mutants are largely unaffected, but ridge cells display altered morphology.
(A-C) Transverse sections through MFFs of Tg(Ola.Actb:Hsa.hras-egfp)vu119-expressing (hras-egfp) wild-type and nrg2a mutant embryos. Green: membrane-bound EGFP, blue: DAPI. (D-E) ET37 EGFP is expressed in MFF cleft cells (cc). ET37-EGFP: green, CellMask: red, DAPI: blue. (A) At 30 hpf, wild-type ridge cells (rc) are roughly cuboidal, with parallel apical and basal domains. The dermal space (ds) has not yet straightened, especially within the apical MFF terminus bounded by the cleft cell (cc). (B, D) By 52 hpf, the dermal space of wild-type embryos has straightened (arrowheads) and has invaginated into the basal side of the cleft cell. Ridge cells have elongated laterally, adopting a flat, planar, epithelial morphology. Their apical and basal domains are essentially parallel. (C, E) In nrg2a mutants, the cleft cell (cc) is present and contains the basal invagination of the dermal space (cleft; E) as in wild-type siblings. In contrast, nrg2a mutant ridge cells have elongated incorrectly and display an abnormal morphology, bulging basally into the dermal space, which acquires a serpentine-like appearance. Scale bar: 10 µm. Abbreviations: cc, cleft cell; rc, ridge cell; arrowheads point to dermal space.