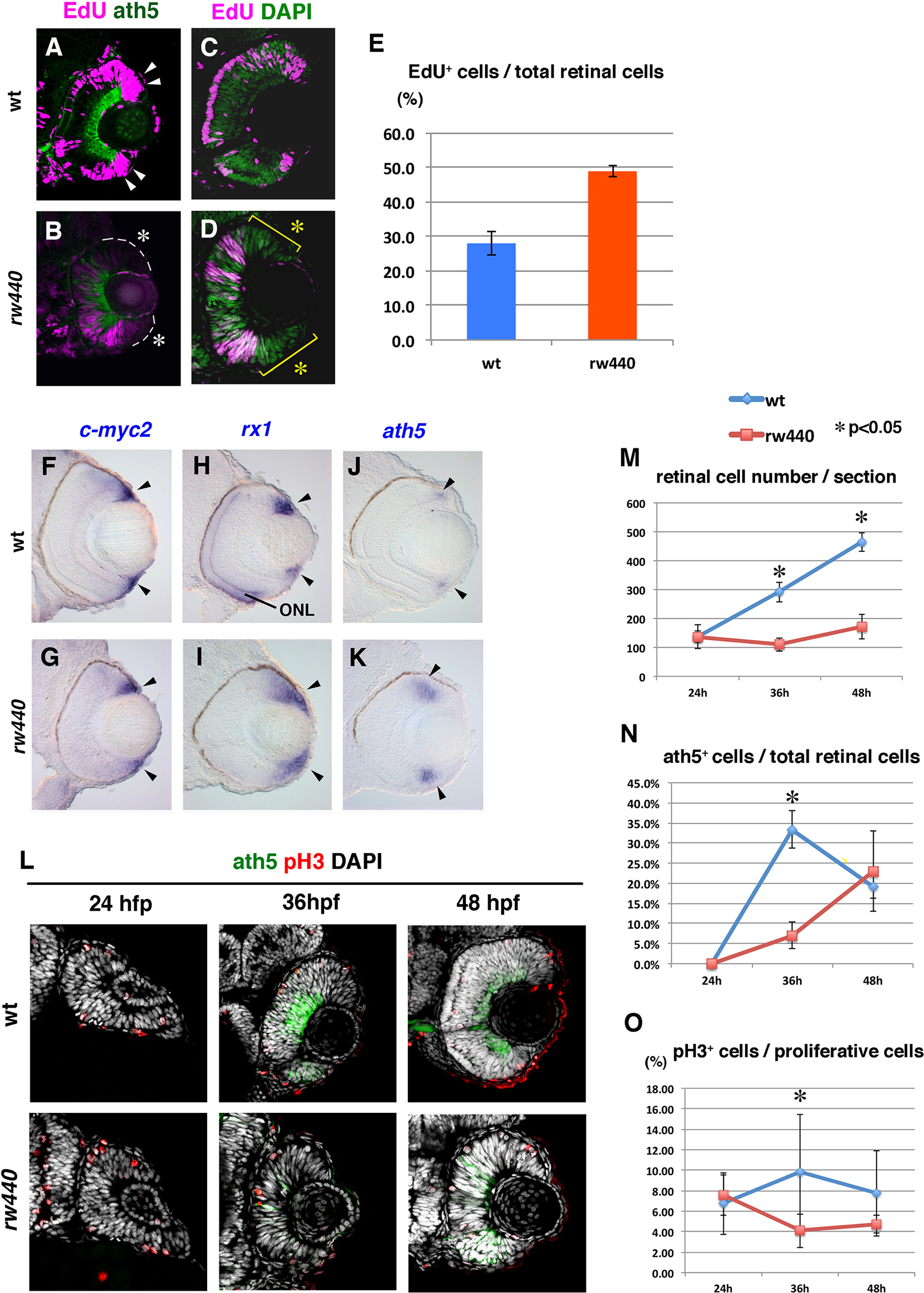
Fig. 4
Cell proliferation and subsequent neurogenesis proceed slowly in the rw440 mutant retina. (A and B) Wild-type (A) and the rw440 mutant (B) retinas labeled with ath5:GFP (green) and EdU (magenta) at 60 hpf. In wild-type retina, EdU incorporation is observed in the retinal CMZ (arrowheads, A) and the peripheral ONL of the central retina. In the rw440 mutant, EdU incorporation is not observed in the retinal CMZ (asterisks, B). A weak EdU incorporation was observed in the central retina, and its pattern was complementary to that of ath5:GFP. (C and D) Wild-type (C) and the rw440 mutant (D) retinas labeled with EdU (magenta) and DAPI (green) at 48 hpf. DAPI labels all nuclei. EdU incorporation is observed in the central retina but not in the CMZ (asterisks, D) in the rw440 mutant. (E) Histogram of the percentage of EdU-positive cells relative to total number of retinal cells. Error bars indicate standard deviation. The difference is statistically significant (p<0.05, t-test). (F–K) In situ hybridization of wild-type and rw440 mutant retinas with c-myc2 (F and G), rx1 (H and I), and ath5 (J and K) RNA probes. All three mRNAs were expressed in the retinal CMZ of wild-type and the rw440 mutant retinas (arrowheads). The rx1 is also expressed in the ONL in wild type (H), but not in the rw440 mutant (I). (L) Labeling of wild-type and the rw440 mutant retinas with anth5:GFP (green), anti-pH3 antibody (red), and DAPI (white) at 24, 36, and 48 hpf. (M) Histogram of the number of retinal cells per section in wild-type and the rw440 mutant retinas. (N) Percentage of ath5:GFP-positive cells relative to total number of retinal cells. (O) The percentage of pH3 positive cells relative to proliferative retinal cells. Error bars shown in (M–O) indicate standard deviation. p*<0.05 (t-test). ONL, outer nuclear layer.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 394(1), Imai, F., Yoshizawa, A., Matsuzaki, A., Oguri, E., Araragi, M., Nishiwaki, Y., Masai, I., Stem-loop binding protein is required for retinal cell proliferation, neurogenesis, and intraretinal axon pathfinding in zebrafish, 94-109, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.