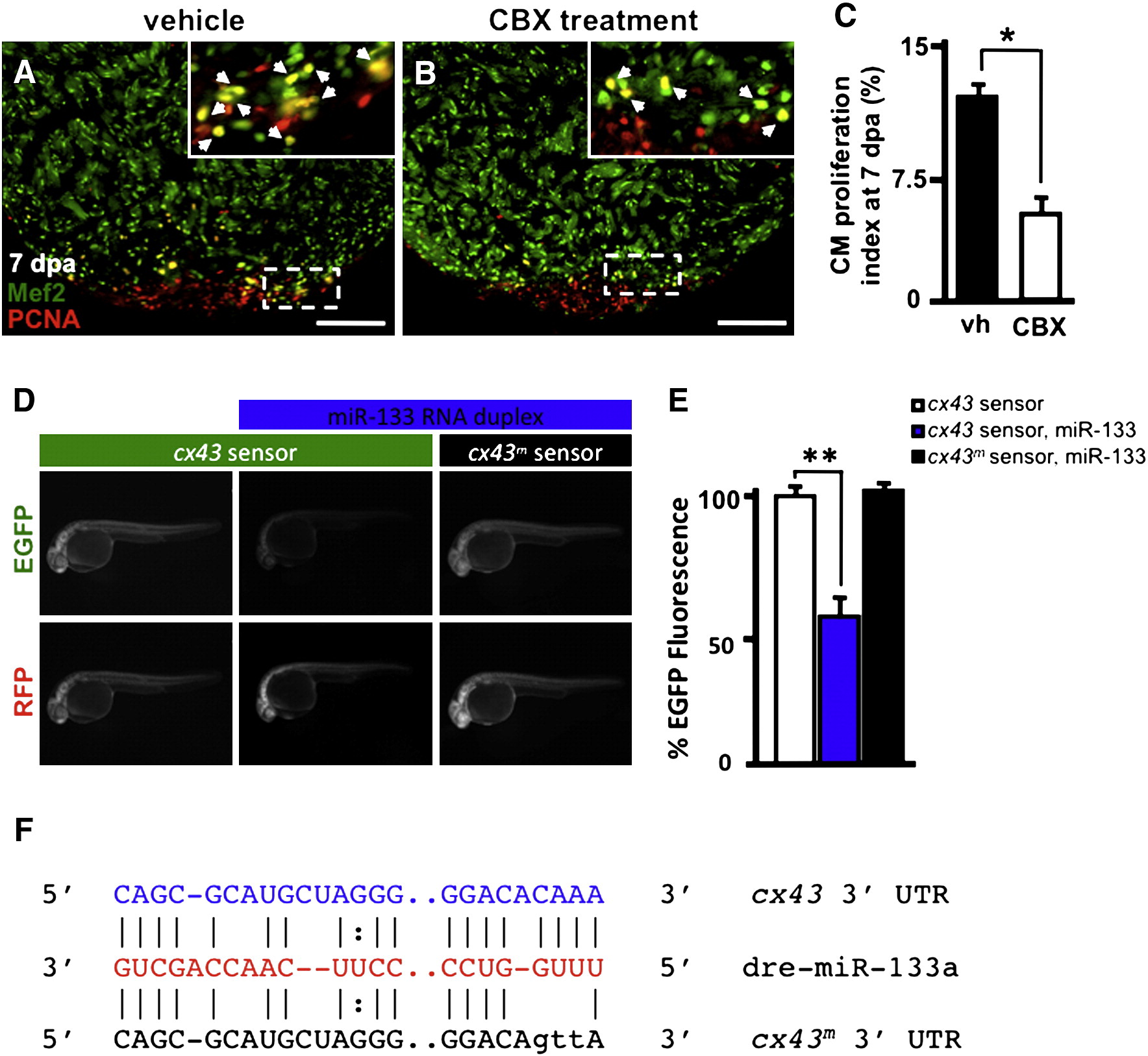
Fig. 6
miR-133 regulates cx43 in vivo. A–B) Wildtype Ekkwill ventricles were resected and allowed to regenerate for 6 days prior to incubation with either vehicle or 50 µM CBX for 24 h. Representative vehicle (vh) and carbenoxolone-treated (CBX) 7 dpa heart sections stained with Mef2 (green) and PCNA (red). Insets in (A, B), high-zoom images of the white dashed rectangle; arrowheads indicate proliferating CMs. C) CM proliferation indices were calculated for each group at 7 dpa. D) Embryos were injected with EGFP-cx43 sensor and mCherry mRNA in the absence (left column) or presence (middle column) of miR-133 RNA duplex. A mutated EGFP-cx43 sensor was also co-injected with miR-133 RNA duplex (right column). E) Quantification of EGFP fluorescence was determined at 24 hpf. F) Alignment of putative miR-133 binding sites in the 32 UTR of cx43. Predictions were based on the Microcosm database. Three point mutations were introduced in the cx43 miR-133 binding site. n = 10–12; Mean ± SEM, Student′s t-test p-value < 0.01 for * and **. hpf = hours post-fertilization. Scale bar in (A–B) represents 100 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 365(2), Yin, V.P., Lepilina, A., Smith, A., and Poss, K.D., Regulation of zebrafish heart regeneration by miR-133, 319-327, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.