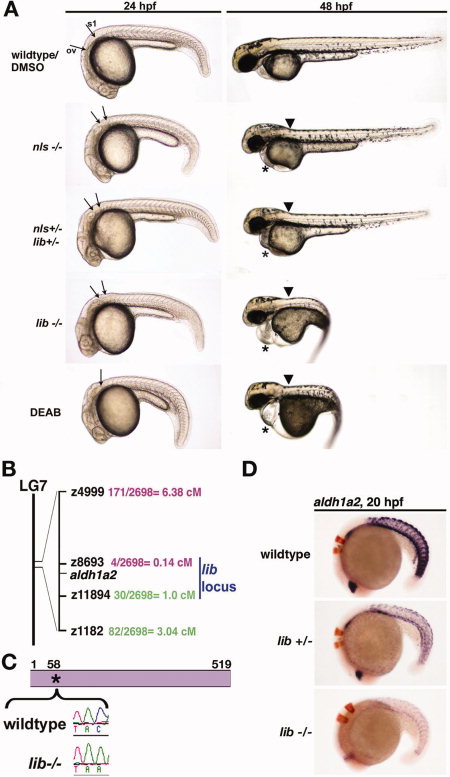
Fig. 4 lib is the most severe genetic model of aldh1a2-deficiency in the zebrafish. A: Lateral views of living 24 and 48 hours postfertilization (hpf) wild-type embryos, nls homozygotes, nls/lib compound heterozygotes, lib homozygotes, and diaminobenzaldehyde (DEAB) -treated wild-types. aldh1a2 mutations are associated with a truncation of the cervical region evident at 24 hpf (arrows indicate the caudal boundary of the otic vesicle [OV] and the rostral boundary of the first somite [S1]). DEAB-treated embryos lack this region, with the OV and S1 located adjacent to each other (indicated by single arrow). At 48 hpf, aldh1a2 mutations are associated with a kink at the head-trunk boundary (black arrow) and pericardial edema (*). Also at 48 hpf, lib and DEAB-treated embryos show pronounced body curvature and develop a lightbulb-shaped yolk compared with wild-types and other aldh1a2 mutants. B: Meiotic mapping placed lib in a genetic interval on linkage group (LG) 7 between z8693 and z11894 that includes aldh1a2. C: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and sequence analysis of aldh1a2 transcripts from lib mutants detected a C → A transversion at nucleotide 174 that is predicted to introduce a Stop codon in lieu of a Tyrosine residue at amino acid position 58 in the 519 amino acid raldh2 enzyme. D: Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of aldh1a2 expression (purple) and krox20 expression (red) shows decreased aldh1a2 transcripts both in lib mutants and lib heterozygote embryos, consistent with nonsense mediated decay.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.