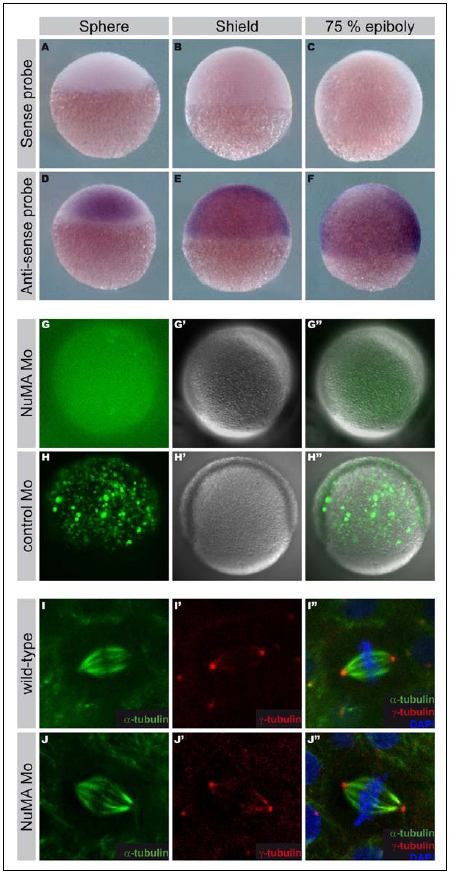
Fig. S2
NuMA is expressed during zebrafish gastrulation.
A-F: Expression of NuMA. In situ hybridization for the NuMA sense probe (A-C) or anti-sense probe (D-F) at the sphere (A, D), shield (B, E) and 75% epiboly (C, F) stages. Animal pole to the top, (C, F) dorsal to the right.
G-H″: The efficiency of the NuMA MO was controlled by showing that the expression of a GFP gene harboring the NuMA MO sequence was abrogated by NuMA MO injection (G-G″) but not by the NuMA control MO (H-H″) in zebrafish embryo injected at the 1 cell stage. GFP channel (G and H), bright field image (G′ and H′) and merge (G″ and H″).
I-J″: Dividing epiblast cells in control (I-I″) and NuMA MO injected embryos (J-J″) stained for α-tubulin (I, I″, J and J″, green), γ-tubulin (I′, I″, J′ and J″, red) and DNA (Hoechst, I″ and J″, blue).
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 19(5), Segalen, M., Johnston, C.A., Martin, C.A., Dumortier, J.G., Prehoda, K.E., David, N.B., Doe, C.Q., and Bellaiche, Y., The Fz-Dsh Planar Cell Polarity Pathway Induces Oriented Cell Division via Mud/NuMA in Drosophila and Zebrafish, 740-752, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell