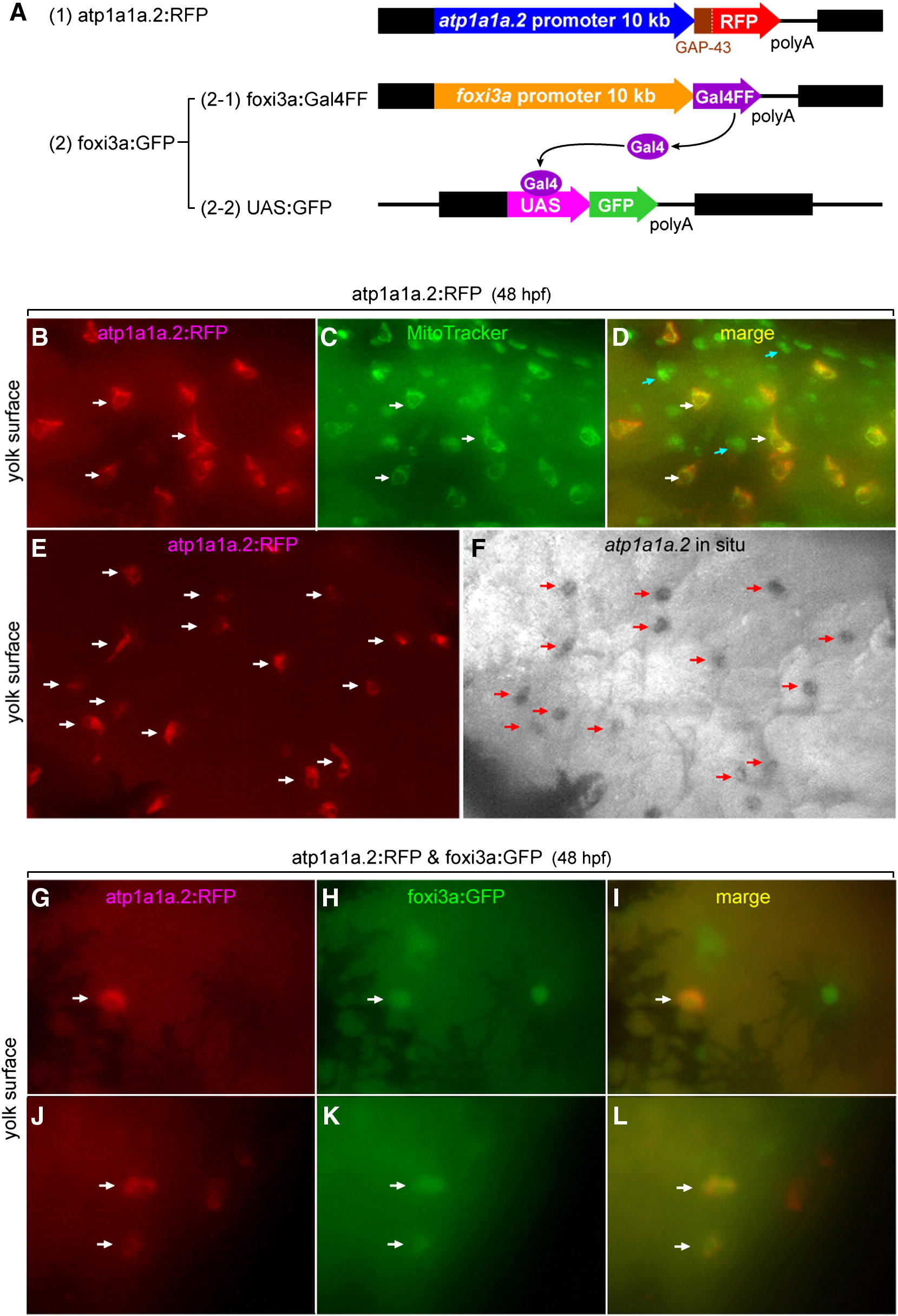
Fig. 9 Lineage tracing showing a foxi3a-positive nature of NaK-MRC precursor. (A) Structures of the three expression vectors used for in vivo RFP labeling of atp1a1a.2-positive cells and in vivo GFP labeling of foxi3a-positive cells. (B–F) Demonstration that RFP is specifically expressed in the NaK-MRC subtype in the atp1a1a.2:RFP transgenic zebrafish line. In C, MitoTracker stains all types of MRCs. Blue arrows in panel D indicate MRCs other than NaK-MRC. (G–L) Examples of coexpression of RFP and GFP in the same cell under the influence of the promoters of the atp1a1a.2 and foxi3agenes in double transgenic zebrafish embryos. Dark areas in panels G–I represent spider-shaped melanocytes.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 329(1), Esaki, M., Hoshijima, K., Nakamura, N., Munakata, K., Tanaka, M., Ookata, K., Asakawa, K., Kawakami, K., Wang, W., Weinberg, E.S., and Hirose, S., Mechanism of development of ionocytes rich in vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase in the skin of zebrafish larvae, 116-129, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.