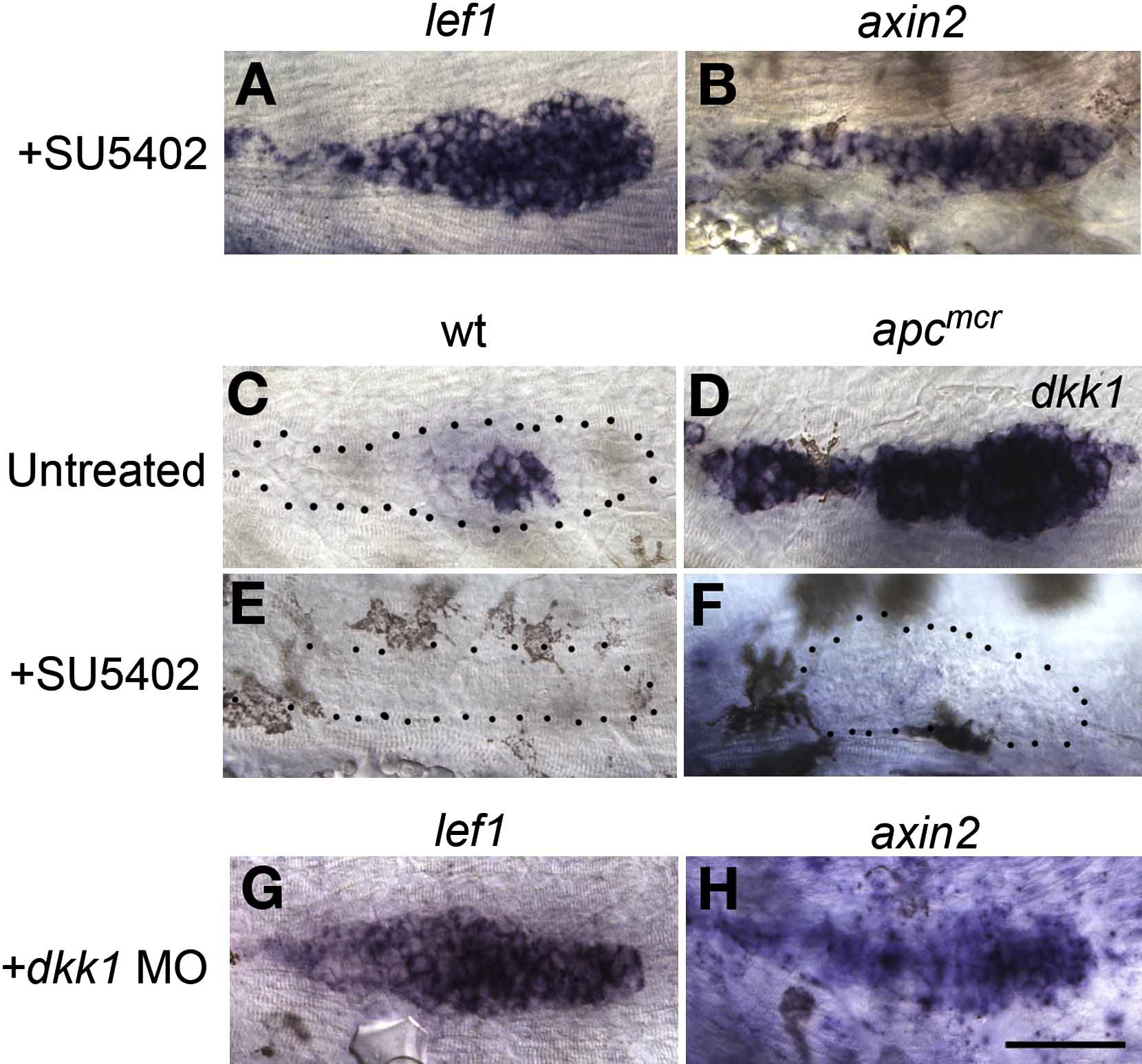
Fig. 5 Fgf Signaling Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling via Induction of dkk1
(A and B) SU5402 treatment leads to ectopic induction of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling targets lef1 and axin2 in 36 hpf embryos.
(C) In WT embryos, dkk1 is expressed adjacent to the unpatterned tip of the primordium.
(D–F) (D) dkk1 is a Fgf target, as it is highly upregulated in apcmcr mutant primordia and is absent in (E) Fgf signaling-depleted WT, as well as in (F) Fgf signaling-depleted apcmcr mutant primordia.
(G and H) Morpholino knockdown of dkk1 causes expansion of lef1 and axin2, similar to loss of Fgf signaling. The scale bar is equal to 40 μM.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 15(5), Aman, A., and Piotrowski, T., Wnt/beta-catenin and Fgf signaling control collective cell migration by restricting chemokine receptor expression, 749-761, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell