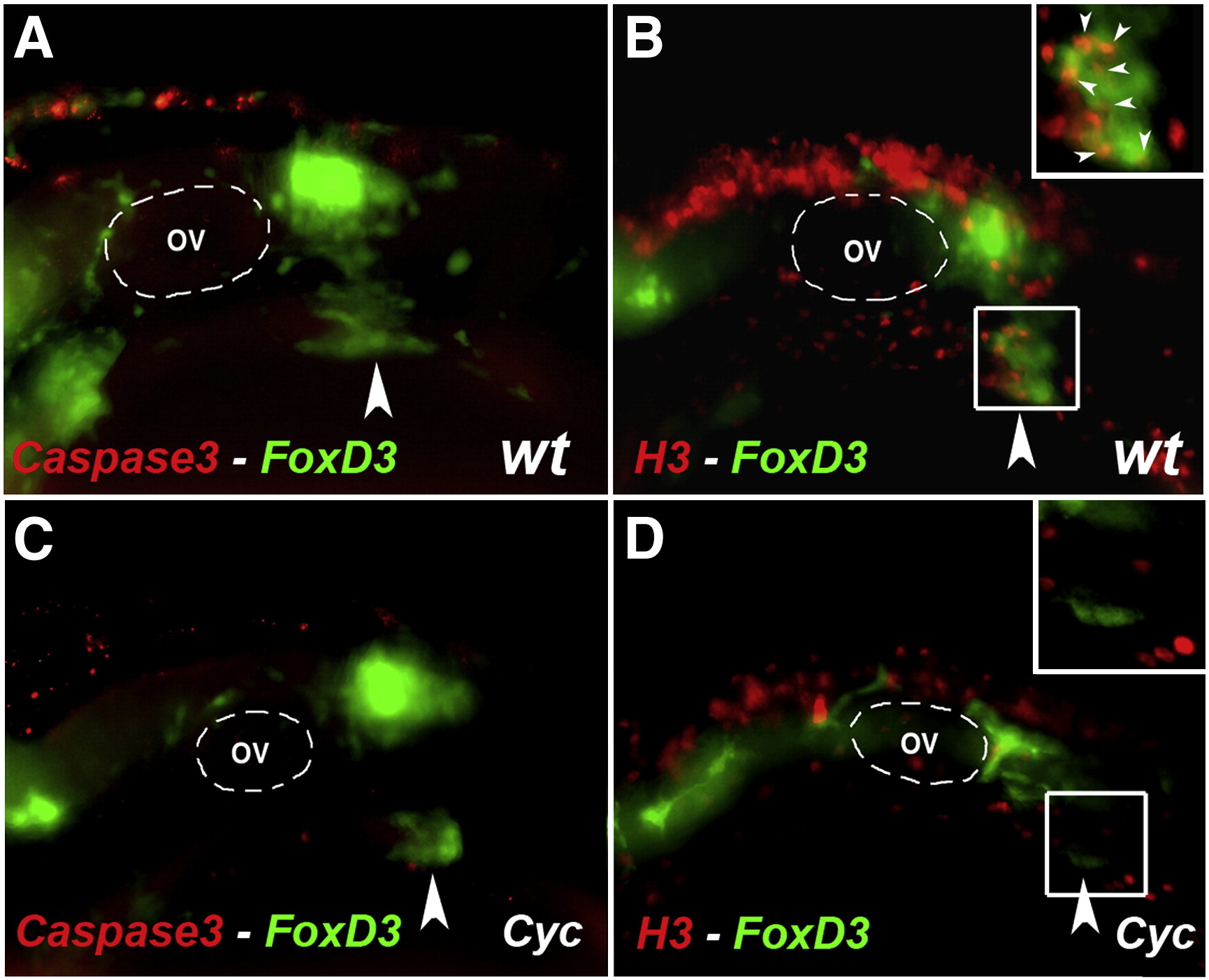
Fig. 7 Cyclopamine treatment causes no change in apoptosis but a decrease proliferation in the vagal NCC and ENS NCC. (A–D) Lateral views of the vagal region of 30 hpf wildtype (A, B) and 24–30 hpf cyclopamine treated (C, D) Foxd3:GFP transgenic embryos. Embryos were immunocytochemically double stained with anti gfp antibody (green) (A–D) to reveal the distribution of vagal NCC and ENS NCC's and anti activated caspase 3 antibody (red) (A, C) to reveal apoptotic cells and anti-phosphohistone H3 (red) (B, D) to reveal proliferating cells. OV (A–D) indicates otic vesicle. Large arrowheads (A–D) indicate the stream of vagal NCC that gives rise to ENS. White boxes (B, D) indicate the region that is shown in close up in the insert. Small white arrowheads (B) indicate proliferating cells. Anterior is to the left.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 318(1), Reichenbach, B., Delalande, J.M., Kolmogorova, E., Prier, A., Nguyen, T., Smith, C.M., Holzschuh, J., and Shepherd, I.T., Endoderm-derived Sonic hedgehog and mesoderm Hand2 expression are required for enteric nervous system development in zebrafish, 52-64, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.