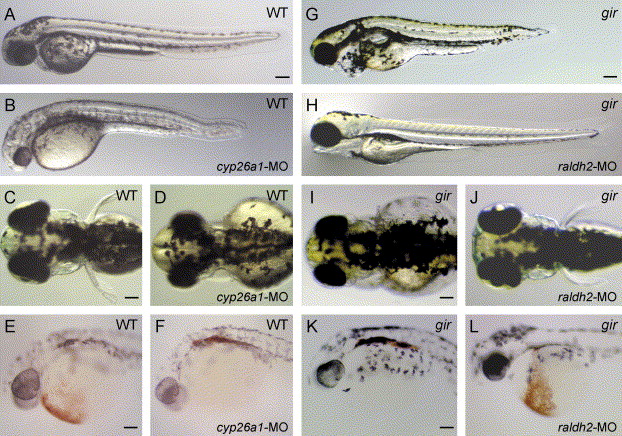
Fig. 4 Morpholino knockdown of cyp26a1 and genetic interaction between gir/cyp26a1 and raldh2. (A, C, and E) Uninjected wild-type control embryos and (B, D, and F) wild-type embryos injected with 1 ng cyp26a1-MO. (A and B) Lateral views of the embryos at 48 hpf. (C and D) Dorsal views of the embryos at 80 hpf. (E and F) o-dianisidine staining of blood cells of the embryos at 28 hpf. Phenotypes of the cyp26a1 morphant are similar to those of the gir mutant. (G, I, and K) Uninjected gir mutants and (H, J, and L) gir mutants injected with 4 ng raldh2-MO. (G and H) Lateral views of the embryos at 80 hpf. (I and J) Dorsal view of the embryos at 80 hpf. (K and L) o-dianisidine staining of blood cells of the embryos at 48 hpf. Genotypes were determined by PCR assay after the photographs had been taken in H, J, and L.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 278(2), Emoto, Y., Wada, H., Okamoto, H., Kudo, A., and Imai, Y., Retinoic acid-metabolizing enzyme Cyp26a1 is essential for determining territories of hindbrain and spinal cord in zebrafish, 415-427, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.