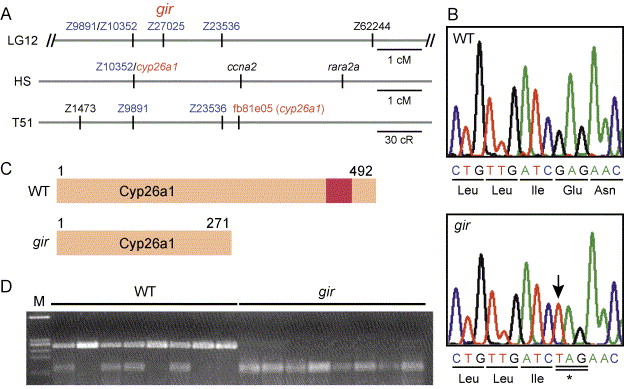
Fig. 3 Molecular isolation of gir. (A) Genetic mapping of gir. In our mapping panel, gir was mapped between Z9891/Z10352 and Z23536 (0.7 cm from Z9891/Z10352 and 1.3 cm from Z23536, n = 150) and at the same position as Z27025. In HS panel, the cyp26a1 gene has been mapped at the same position as Z10352. In the T51 panel, fb81e05, an EST clone of cyp26a1, has been mapped near Z23536. (B) The gir mutant carries a nonsense mutation in the cyp26a1 gene at position 814. The mutated nucleotide is indicated by the arrow. (C) Schematic representation of the Cyp26a1 protein and its truncated form in the gir mutant. The red box represents a heme-binding motif, which is conserved among cytochrome P450s. (D) The cyp26a1 gene is linked to gir. A cyp26a1 fragment was amplified from the wild-type (+/+ or gir/+) and gir mutant embryos and digested with XbaI, which cleaves the mutant cyp26a1 allele, but not the wild-type allele. All gir mutants had only the mutant cyp26a1 allele (no recombinants among 356 meioses), indicating that cyp26a1 is tightly linked to gir.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 278(2), Emoto, Y., Wada, H., Okamoto, H., Kudo, A., and Imai, Y., Retinoic acid-metabolizing enzyme Cyp26a1 is essential for determining territories of hindbrain and spinal cord in zebrafish, 415-427, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.