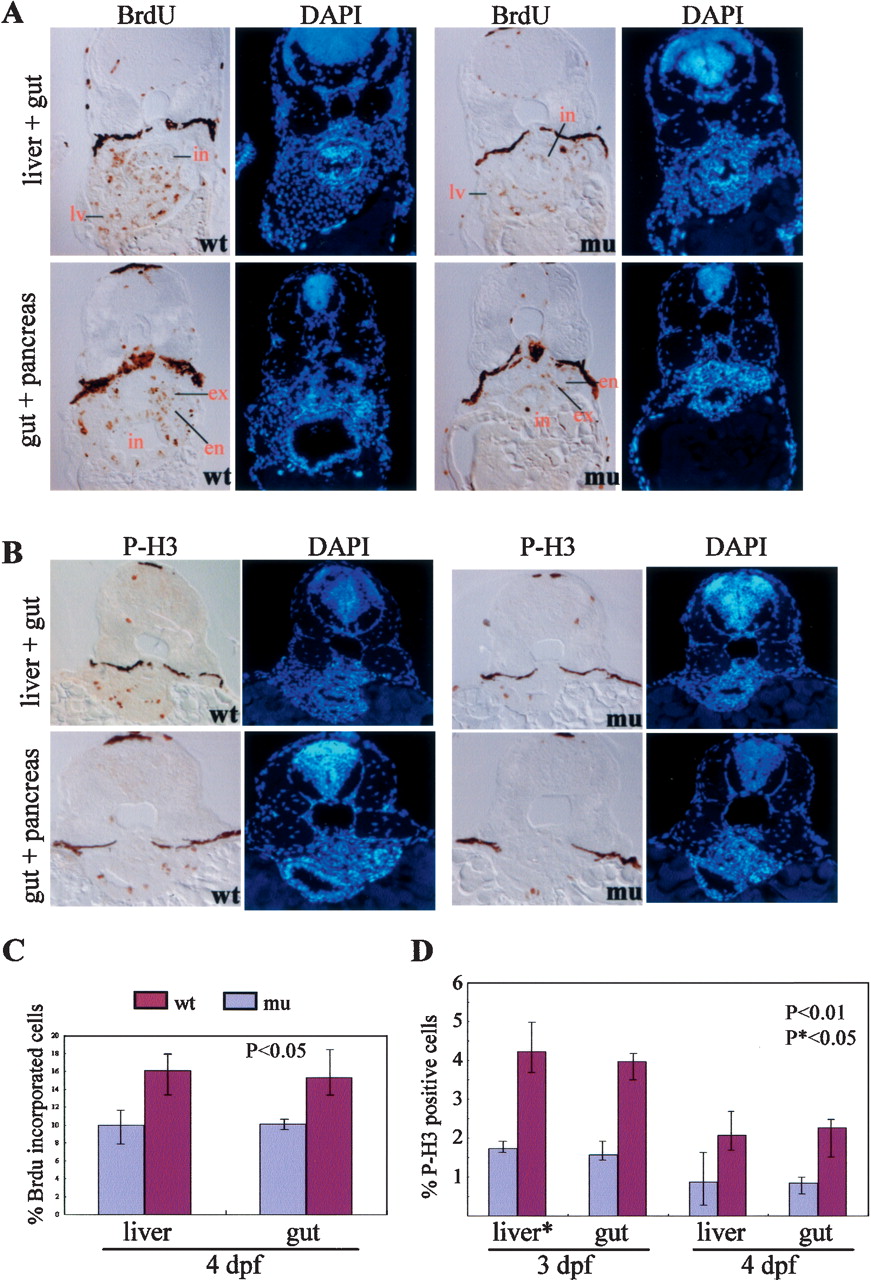
Fig. 7 The defhi429 mutant phenotype is caused by compromised cell proliferation. (A,C) BrdU labeling revealed that, at 4 dpf, the number and ratio of cells entering the G1-to-S-phase transition was significantly reduced in the digestive organs of the defhi429 mutant (mu) when compared with the wild type (wt). (Top panel) Cross-sectioning through liver (lv) and intestine (in). (Bottom panel) Cross-sectioning through pancreas and intestine (in). The BrdU incorporation ratios shown in C were obtained by counting BrdU-labeled cells versus total cells in a specific organ (e.g., liver) in sections from seven wild-type and seven mutant embryos, respectively. (en) Endocrine pancreas; (ex) exocrine pancreas. (B,D) At 3 and 4 dpf, histochemical staining using anti-phosphorylated histone 3 (anti-P-H3) revealed that the number and ratio of cells entering G2 to M phase was drastically reduced in the digestive organs of the defhi429 mutant (mu) when compared with the wild type (wt). The ratios of P-H3-positive cells shown in D were obtained by counting P-H3-positive cells versus total cells in a specific organ (e.g., liver) in sections from three wild-type and three mutant embryos, respectively.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
In addition, ZFIN would like to thank the authors for kindly granting us permission to reproduce their figures.
Full text @ Genes & Dev.