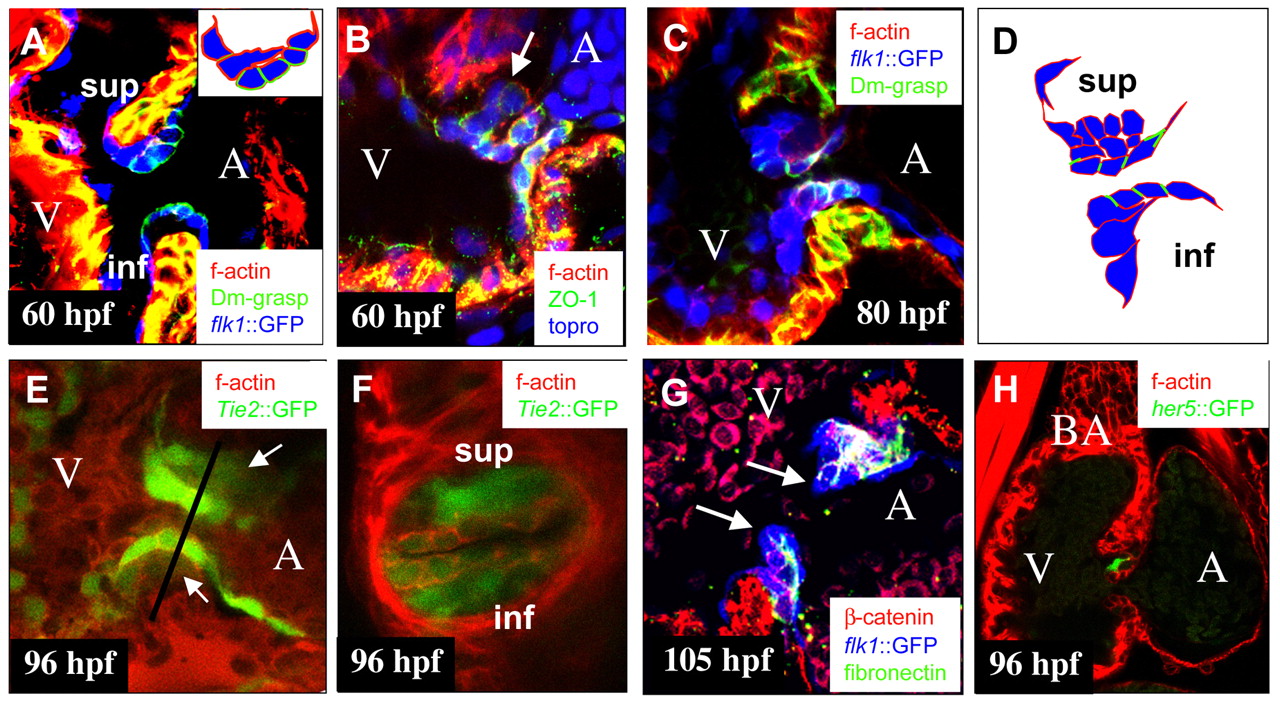
Fig. 2 Wild-type endocardial cushion morphogenesis. Confocal images of the AV canal at 60 (A,B), 80 (C), 96 (E,F) and 105 hpf (G), and of the heart at 96 hpf (H). (A,C,G) Tg(flk1:EGFP)s843 (pseudo-colored blue) embryo immunostained for Dm-grasp (pseudo-colored green) and stained with rhodamine phalloidin (red) (A,C) or immunostained for fibronectin (pseudo-colored green) and ß catenin (red) (G). (E,F) Tg(Tie2:EGFP)s849 (green) embryo stained with rhodamine phalloidin (red). (B) Embryo immunostained for ZO-1 (green) and stained with topro (blue) and rhodamine phalloidin (red). (H) Tg(0.7her5:EGFP)ne2067 (green) embryo stained with rhodamine phalloidin (red). (A) AV endocardial cell at the ventricular border has extended into the ECM and is reaching the base of cells close to the atrial border. Inset shows schematic drawing of AV endocardial cells of the superior AV EC. (B) Cells, such as the one indicated by the arrow, located in the ECM between the endocardium and myocardium have downregulated and delocalized ZO-1, indicating an epithelial to mesenchymal transition. (C) At 80 hpf, the superior AV EC consisting of mesenchymal cells has formed. In the inferior ECFR at this time, AV endocardial cells at the ventricular border start extending cellular protrusions into the ECM. (D) Schematic representation of AV canal endocardial cells as shown in C. (E,F) By 96 hpf, both superior and inferior AV ECs (arrows in E) have formed. Line in E indicates the plane of the transverse section shown in F. (G) By 105 hpf, ECs have elongated and start projecting into the ventricular lumen. Cushion extensions (arrows) consist of two layers of cells separated by a layer of fibronectin-containing ECM. (H) Expression of Tg(0.7her5:EGFP)ne2067 in a subset of cells in elongating ECs. A, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; V, ventricle; inf, inferior AV EC; sup: superior AV EC.