Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240625-47
- Publication
- Jędrychowska et al., 2024 - Mutant analysis of Kcng4b reveals how the different functional states of the voltage-gated potassium channel regulate ear development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
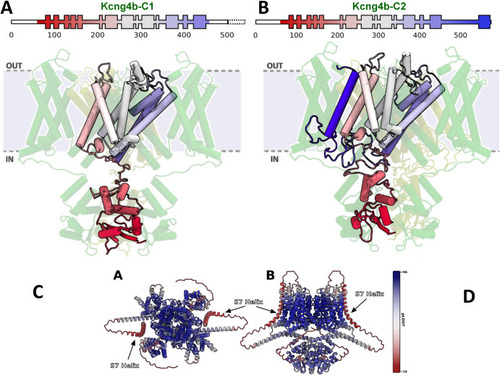
Modelling of Kcng4b/Kv6.4 mutant monomers. Kcng4b-C1 (A), Kcng4b-C2 (B–D). IN, OUT – internal and external space. The deleted C-terminal region of Kcng4b-C1 is indicated by the dashed box. The additional transmembrane domain of Kcng4b-C2 (S7) is in dark blue. (C) Top and (D) side view of structure of Kv1.2–2.1 + Kcng4b tetramer as predicted by AlphaFold Multimer v3, colored by per-residue model confidence score (pLDDT). Two monomers of each protein were used to form the tetramer, analogous to the simulated model. AlphaFold clearly predicts the S7 helix in the membrane, bound to the core of the tetramer. Confidence score of the S7 helix prediction is low, which is expected from the terminus of the protein and a sequence that was not under evolutionary pressure. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 513, Jędrychowska, J., Vardanyan, V., Wieczor, M., Marciniak, A., Czub, J., Amini, R., Jain, R., Shen, H., Choi, H., Kuznicki, J., Korzh, V., Mutant analysis of Kcng4b reveals how the different functional states of the voltage-gated potassium channel regulate ear development, 50-62, Copyright (2024) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.