Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240517-30
- Publication
- Zhu et al., 2024 - Allelic heterogeneity of TTNtv cardiomyopathy can be modeled in adult zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
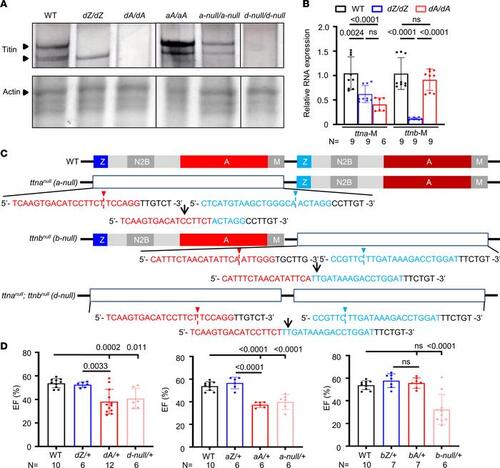
ttn-null mutants manifest similar phenotypes to ttntv-A but not ttntv-Z mutants. (A) Protein analysis of 2 dpf larvae of WT, dZ/dZ, dA/dA, aA/aA, a-null/a-null, and d-null/d-null mutants. The upper lane shows silver staining of a 2% SDS-agarose gel. The same protein lysates were then analyzed by Coomassie blue staining with a 12.5% SDS-PAGE system, as shown in the bottom lane. The expression of Actin was used as a loading control. (B) ttna and ttnb mRNA expression levels in dA/dA and dZ/dZ embryos, as revealed by quantitative PCR using primer pairs that recognize the M-line exons of ttna and ttnb, respectively. (C) Schematics of the location of sgRNAs that were used to generate the large deletions in ttn-a-null, ttn-b-null, and ttn-d-null. The red and blue sequences are sgRNAs on either side. Arrowheads indicate the cutting sites, and the resulting genome sequence is listed below. (D) High-frequency echocardiography was performed in adult zebrafish at 6 months to quantify the ejection fraction. One-way ANOVA was used to compare multiple groups for each mutation. Data are presented as mean ± SD. |