Figure 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240317-3
- Publication
- Brugger et al., 2024 - Bi-allelic variants in SNF8 cause a disease spectrum ranging from severe developmental and epileptic encephalopathy to syndromic optic atrophy
- Other Figures
- (all 8)
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
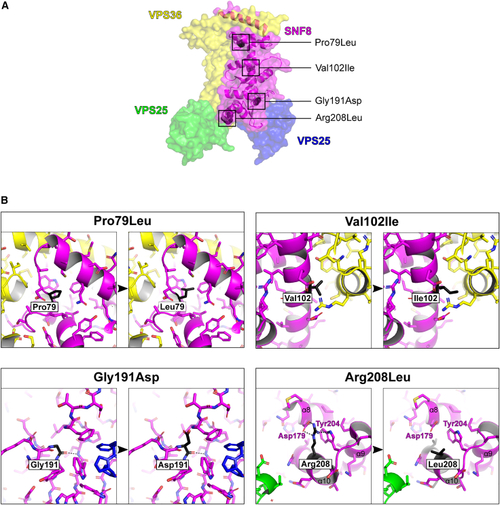
Representation of the 3D structure of SNF8 with the observed missense variants (A) The surface rendering of human ESCRT II complex (PDB: (B) Magnified view of the residues affected by the reported missense variants. The affected residues are shown in black and labeled accordingly. Hydrogen bonds involving affected residues are depicted as dashed black lines. The variants p.Pro79Leu and p.Gly191Asp introduce larger residues that lead to steric clashes with surrounding residues and likely affect the conformation and stability of SNF8. In contrast, the p.Arg208Leu variant replaces the long and charged arginine with a short and hydrophobic leucine, resulting in a loss of interaction with aspartic acid 179 and tryptophan 204, thus most likely also affecting the conformation and stability of SNF8. The most conservative amino acid substitution with the least impact is p.Val102Ile, in which the small hydrophobic valine is replaced by a slightly larger (one atom) hydrophobic isoleucine. |