Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240103-1
- Publication
- Lin et al., 2024 - RPTOR blockade suppresses brain metastases of NSCLC by interfering the ceramide metabolism via hijacking YY1 binding
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
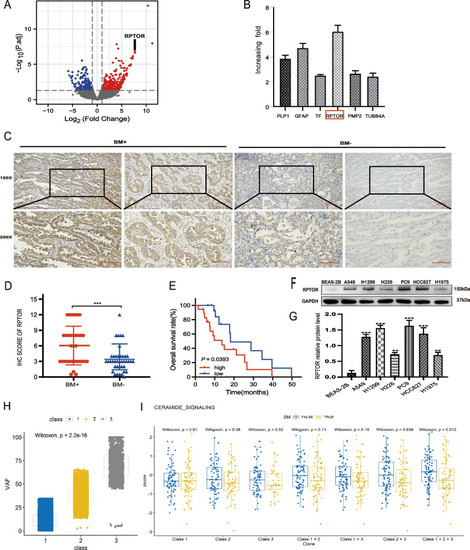
Association of high RPTOR expression or the ceramide pathway with NSCLC-BM. |