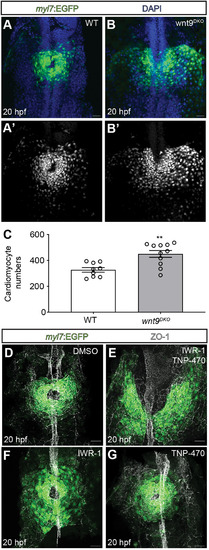
Wnt9a/b signal via canonical and non-canonical pathways during cardiac cone formation. (A-C) Quantification of cardiomyocyte numbers in wildtype versus wnt9DKO mutants during cardiac cone formation. Cardiomyocyte numbers increase in wnt9DKO mutants (wildtype, n=9 embryos; wnt9DKO, n=11 embryos). Data are mean±s.e.m. Dots represent single values (**P<0.01; two-tailed, unpaired Student's t-test). (D-G) Maximum projections of confocal z-scans with ventral views of cardiomyocyte progenitor cells during cardiac cone formation. In DMSO-treated control embryos, the heart cone has formed by 20 hpf (D) whereas in IWR-1- and TNP-470-treated embryos, cardiomyocyte progenitor cells have not reached the embryonic midline and failed to fuse into a heart cone (E; n=21/21 embryos analyzed). Heart cones of embryos treated only with IWR-1 (F; n=6/6 embryos analyzed) or TNP-470 (G; n=11/11 embryos analyzed) have no anterior fusion defects. The treatment with IWR-1, TNP-470, their combination or DMSO (control) was carried out from 14 to 20 hpf. The embryonic midline is labeled for ZO-1. Scale bars: 30 µm.
|