Figure 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221118-192
- Publication
- Ding et al., 2022 - A phenotype-based forward genetic screen identifies Dnajb6 as a sick sinus syndrome gene
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
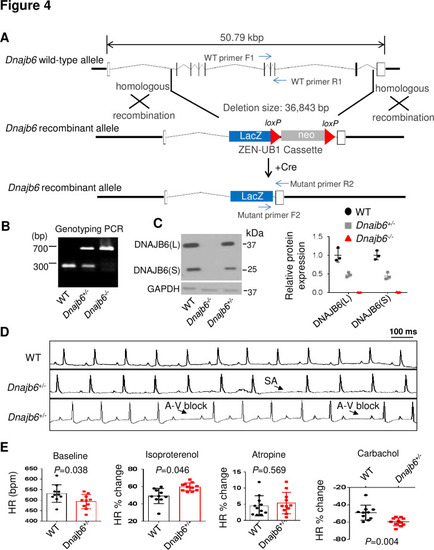
Dnajb6+/- mice exhibited increased incidence of SA and AVB and impaired response to autonomic stimuli. (A) Schematics of the Dnajb6 knockout (KO) mice. The insertion of Velocigene cassette ZEN-Ub1 created a deletion of 36,843 bp nucleotides spanning from the first to the last intron of the Dnajb6 gene at the Chromosome 5. The neomycin selection cassette was excised after crossed to a Cre expression line. (B) Representative DNA gel images of PCR genotyping for identifying WT (300 bp), Dnajb6+/- heterozygous (hets), and Dnajb6-/-homozygous (homo) mutant alleles . (C) Western blotting and quantification of DNAJB6 short (S) and long (L) protein expression in WT and Dnajb6 mutants. N=3 animal per group. (D) Shown are representative ECG recordings results showing SA and AVB phenotypes detected in the Dnajb6+/- mice at 6 months. (E) The Dnajb6+/- mice manifests impaired response to different autonomic stimuli. N=10–12 mice per group, unpaired student’s t-test. SA, sinus arrest. AVB, atrioventricular block. |