Figure 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221030-34
- Publication
- Preiß et al., 2022 - Regulation of Nodal signaling propagation by receptor interactions and positive feedback
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
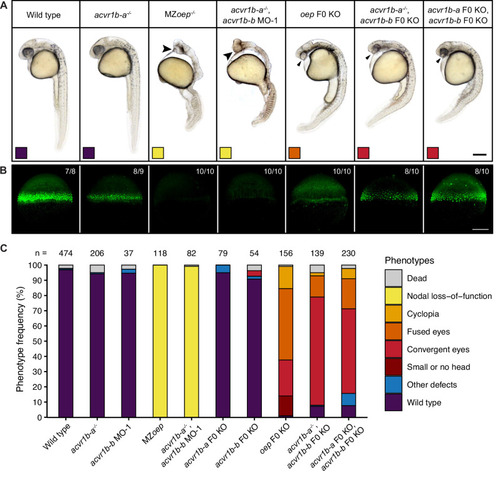
Phenotypes of wild-type, MZoep and oep CRISPR F0 KO embryos compared to embryos depleted of either or both acvr1b-a and acvr1b-b using morpholino KDs, CRISPR F0 KOs and mutants. (A) Lateral view of embryos of the indicated condition approximately 28–31 hpf. Large arrowheads point to a single cyclopic eye, small arrowheads to fused or convergent eyes. Boxes indicate the phenotype class according to the scheme presented in (C). Scale bar represents 250 µm. (B) Nodal signaling visualized by pSmad2/3 immunostaining in embryos of the indicated condition (A) at 50% epiboly. Maximum intensity projections show lateral views. The number of embryos with the presented phenotype is indicated. Scale bar represents 200 µm. (C) Frequency of phenotypes observed in embryos of the indicated condition 1 dpf. n indicates the number of analyzed embryos. Note that one of the gRNAs used for acvr1b-b F0 KO has acvr1b-a as a predicted off-target, likely explaining the rare occurrences of the convergent eyes phenotype (see Materials and methods). See the Figure 3—source data 1 file for source data.
|