Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-221018-225
- Publication
- Cai et al., 2021 - Dhx15 regulates zebrafish definitive hematopoiesis through the unfolded protein response pathway
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
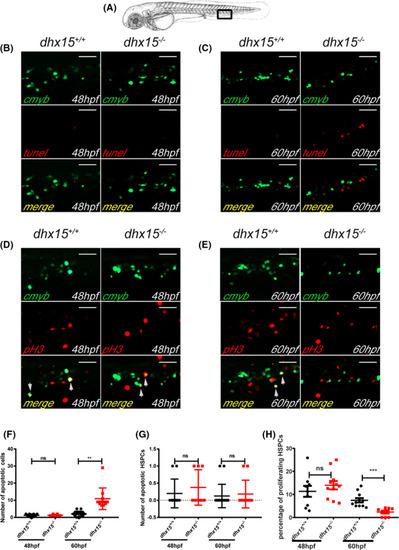
Abated proliferation but not excessive apoptosis of HSPCs is observed in dhx15−/− zebrafish. A, Schematic indicates the area of the imaging in the tail (CHT), outlined by the black box. B, C, Fluorescence images of the cmyb and apoptotic cells in CHT of dhx15+/+; Tg(cmyb:gfp) and dhx15−/−; Tg(cmyb:gfp) zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) (B) and 60 hpf (C). D, E, Fluorescence images of pH3 and cmyb positive cells in CHT of dhx15+/+; Tg(cmyb:gfp) and dhx15−/−; Tg(cmyb:gfp) zebrafish embryos at 48 hpf (D) and 60 hpf (E). F, Number of apoptotic cells in CHT at 48 hpf (wildtype, 1.2 ± 0.2494, n = 10; dhx15−/− embryos, 1.25 ± 0.1637, n = 8; P > .05, Student’s t test) and 60 hpf (wildtype, 2.063 ± 0.3923, n = 16; dhx15−/− embryos, 10.91 ± 1.944, n = 11; P < .005, Student’s t test). G, Number of apoptotic HSPCs in CHT at 48 hpf (wildtype, 0.2 ± 0.1333, n = 10; dhx15−/− embryos, 0.375 ± 0.183, n = 8; P > .05, Student’s t test) and 60 hpf (wildtype, 0.125 ± 0.08539, n = 16; dhx15−/− embryos, 0.1818 ± 0.122, n = 11; P > .05, Student’s t test). H, Percentages of proliferating HSPCs in CHT at 48 hpf (wildtype, 11.34 ± 2.379, n = 9; dhx15−/− embryos, 13.98 ± 1.829, n = 11; P > .05, Student’s t test) and 60 hpf (wildtype, 7.464 ± 0.9413, n = 11; dhx15−/− embryos, 2.367 ± 0.6178, n = 9; P < .0005, Student’s t test). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .0005. Scale bar = 40 μm. CHT, caudal hematopoietic tissue; hpf, hours post fertilization; HSPCs, hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells; ns, not significant; pH3, pospho‐histone H3 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Pec-fin |