Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-220307-10
- Publication
- Kam et al., 2022 - Rough and smooth variants of Mycobacterium abscessus are differentially controlled by host immunity during chronic infection of adult zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
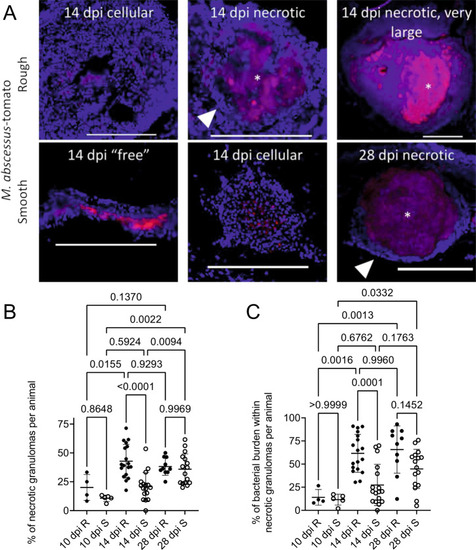
Granuloma histopathology is accelerated during M. abscessus R infection compared to S.
A Stereotypical examples of bacterial lesions from DAPI-stained sections from adult zebrafish infected with M. abscessus expressing tdTomato. Top row infected with the rough variant, bottom row infected with the smooth variant, timepoints as indicated. Images are representative of the two experimental replicates quantified in B, C. Scale bars indicate 200 μm. Filled arrowheads indicate epithelised macrophage nuclei forming a stereotypical concentric layer surrounding the mycobacterial core of necrotic granulomas, * indicate necrotic cores. B Quantification of bacterial lesion necrosis in adult zebrafish infected with approximately 105 CFU M. abscessus. Each data point represents the proportion of lesions from a single animal. C Quantification of bacterial burden stratified by lesion necrosis in adult zebrafish infected with either the R or the S variant of M. abscessus. Each data point represents the proportion of lesions from a single animal. Total individual lesions and animals analysed in B and C pooled from two experimental replicates (necrotic/unorganised/animals): 10 dpi R (37/228/4); 10 dpi S (107/788/5); 14 dpi R (299/447/18); 14 dpi S (111/539/17); 28 dpi R (149/217/10); 28 dpi S (382/603/16). Statistical testing by two-sided ANOVA. Data are presented as mean values ± SD. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |