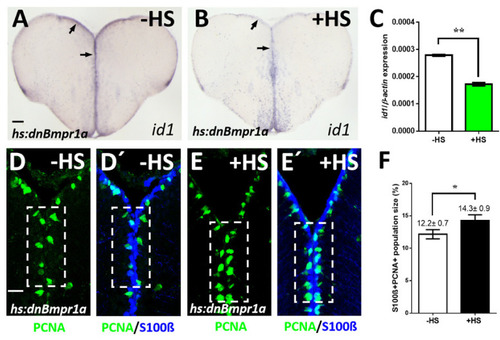
Inhibition of BMP signaling leads to a reduction of id1 expression and an increase of proliferating NSCs. (A,B) Reduced id1 expression after inhibition of the BMP pathway by heat-shock of Tg(hs:dnBmpr1a) animals. Black arrows point at the expression of id1 in the ventricular zone of Tg(hs:dnBmpr1a) animals without (A, -HS) and with heat-shock (B, +HS). (C) RT-qPCR quantification of id1 mRNA expression shown in A-B indicates that inhibition of BMP signaling leads to a significant reduction of id1 expression. (D–E’) Immunohistochemistry on telencephalic transverse sections of Tg(hs:dnBmpr1a) animals for NSCs (S100β, blue) and proliferating cells (PCNA, green), focusing on the ventricular zone of the dorsal telencephalon. The number of proliferating NSCs (PCNA+/S100β+ cells) is increased after heat-shock (compare dashed white boxed area in (D,D’) to (E,E’)). (F) Quantification of the population size of PCNA+/S100β+ cells exhibiting a significant increase in heat-shocked (+HS) compared to non-heat-shocked (-HS) telencephala. Significance is indicated by asterisks: * 0.01 ≤ p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. n = 3 brains (C), n = 15 sections (F). Scale bar = 20 μm (D–E’), 100 μm (A,B). HS: heat-shock.
|

