Figure 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210801-62
- Publication
- Gawel et al., 2021 - 6-Gingerol, a Major Constituent of Zingiber officinale Rhizoma, Exerts Anticonvulsant Activity in the Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizure Model in Larval Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
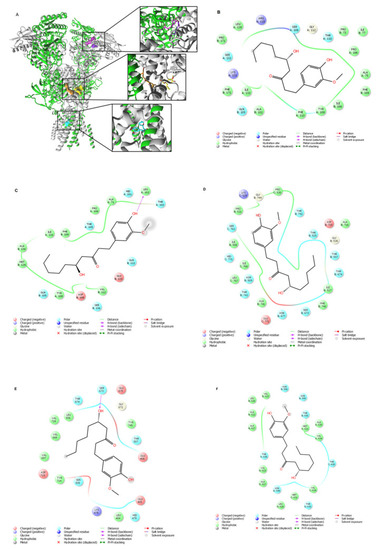
Molecular docking of 6-GIN to the GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor. (A) 6-GIN binding sites (surface model) are located at the ATD (magenta and purple), the LBD (yellow and orange) and the TMD (cyan) of the GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor. More specifically, molecular docking results suggested two different orientations of 6-GIN at ATD, a high-affinity site (magenta) located at the GluN1/GluN2B interface and a low-affinity site (purple) within the GluN2B subunit. In addition, 6-GIN may interact with the glutamate binding site (at the LBD). Orientation 1 presents a higher affinity site (orange) at the GluN1/GluN2B LBD interface, and orientation 2 presents a lower affinity pose (yellow) located within the LBD of the GluN2B subunit. Finally, the 6-GIN interacts within the ion channel (at the TMD) of the GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor. (B,C) 2D views of 6-GIN interacting with the high-affinity site and low-affinity site at the ATD, respectively. (D,E) 2D views of 6-GIN interacting with the higher-affinity as well as lower-affinity sites at the LBD, respectively. (F) 2D view of the 6-GIN interactions within the ion channel pore of the GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor. The GluN1 subunits are shown in green, and the GluN2B subunits are depicted in grey. The residues involved in 6-GIN binding are presented in panels (B–F) (2D views) and included in Table 1. Hydrogen bonds are marked with pink arrows, residues involved in hydrophobic interactions are shown in green, polar in blue, and charged residues involved in binding are shown in red. |