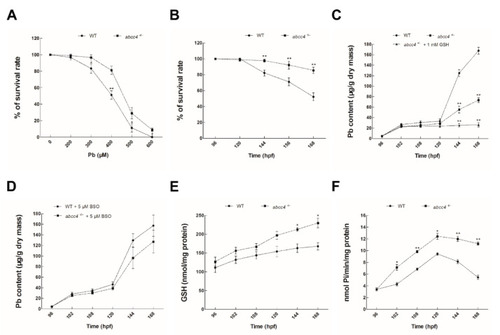
Functional characterization of Abcc4 in lead detoxification in transgenic zebrafish. (A) Survival rates of abcc4-transgenic and WT embryos were monitored after treatment with different concentrations of lead (0–600 μM) from 96 to 168 hpf. (B) Survival rates of abcc4-transgenic and WT larvae were detected after exposure to 400 μM lead for 72 h. (C) Contents of lead in abcc4-transgenic and WT larvae after exposure to 10 μM lead with or without 1 mM glutathione (GSH) at the indicated exposure time points. (D) Contents of lead in abcc4-transgenic and WT larvae at the indicated exposure time points after treatment with a medium containing 10 μM lead and simultaneously with 5 μM buthionine sulfoximine (BSO), an inhibitor of GSH biosynthesis. (E) Intracellular GSH contents in abcc4-transgenic and WT larvae exposed to 10 μM lead at the indicated exposure time points. (F) ATPase activities as shown by inorganic phosphate (Pi) levels in abcc4-transgenic and WT larvae after treatment with 10 μM lead at the indicated exposure time points. Values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences are indicated by * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.
|

