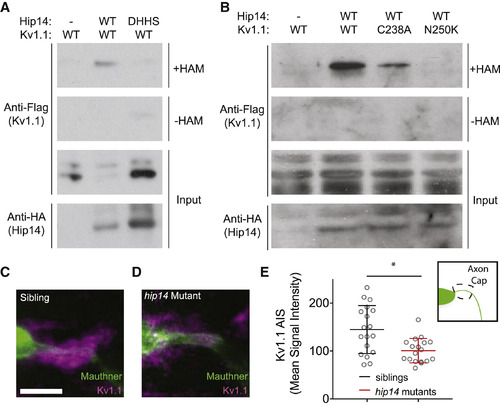
Hip14 Palmitoylates Kv1.1 and Regulates Its Localization In Vivo (A and B) Acyl biotin exchange assays, in which Kv1.1-FLAG ± Hip14-HA are transfected into HEK cells. Only in the presence of WT Hip14-HA, WT Kv1.1-FLAG, and hydroxylamine (+HAM) does robust palmitoylation of Kv1.1-FLAG occur. Samples without hydroxylamine (−HAM) are negative controls for the ABE reactions. (A) Mutation of the Hip14 DHHC domain disrupts Kv1.1 palmitoylation. (B) Mutations in Kv1.1 disrupt its palmitoylation. (C) Immunohistochemical labeling of the Mauthner cell (green) and Kv1.1 (magenta) in gffDMC130a; uas:gap43:citrine sibling, using chicken anti-GFP and rabbit anti-Kv1.1 antibodies. Note the bright localization of Kv1.1 to the axon cap: synaptic inputs from spiral fiber neurons onto Mauthner cell AIS are shown. (D) Immunohistochemical labeling of a hip14 mutant animal as in (C). Note the reduction in Kv1.1 signal at the axon cap. (E) Quantification of Kv1.1 signal in mutants as compared to WT. Mean signal intensity, pixel intensity for axon cap region of interest (inset) divided by axon cap area. Unpaired t test; p = 0.0021. Scale bar, 10 μm. Mean ± SD; n = 18 axon caps per genotype (n ≤ 2 axon caps per animal). See also Figure S3.
|

